Dystonia is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that result in abnormal postures and repetitive movements. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s functional abilities and quality of life. However, physical therapy has emerged as a valuable treatment modality for dystonia, offering services aimed at improving function and providing relief to those affected by this condition.
Consider the case of Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experienced persistent neck spasms, causing her head to tilt uncontrollably to one side. This debilitating symptom severely limited her ability to engage in daily activities such as driving or working on a computer. Seeking assistance, Sarah was referred to a specialized physical therapist who implemented various techniques tailored to address her specific needs and goals. Through targeted exercises, manual therapies, and sensory retraining, Sarah gradually achieved improved control over her muscles’ movements, resulting in enhanced functionality and reduced pain.
Physical therapy interventions for individuals with dystonia encompass diverse approaches designed to alleviate symptoms while promoting optimal motor performance. This article explores the comprehensive array of services offered within physical therapy practice settings that contribute towards enhancing function and alleviating distress associated with dystonia. By delving into the benefits of these interventions, we aim to shed light on how individuals with dystonia can benefit from physical therapy intervention.
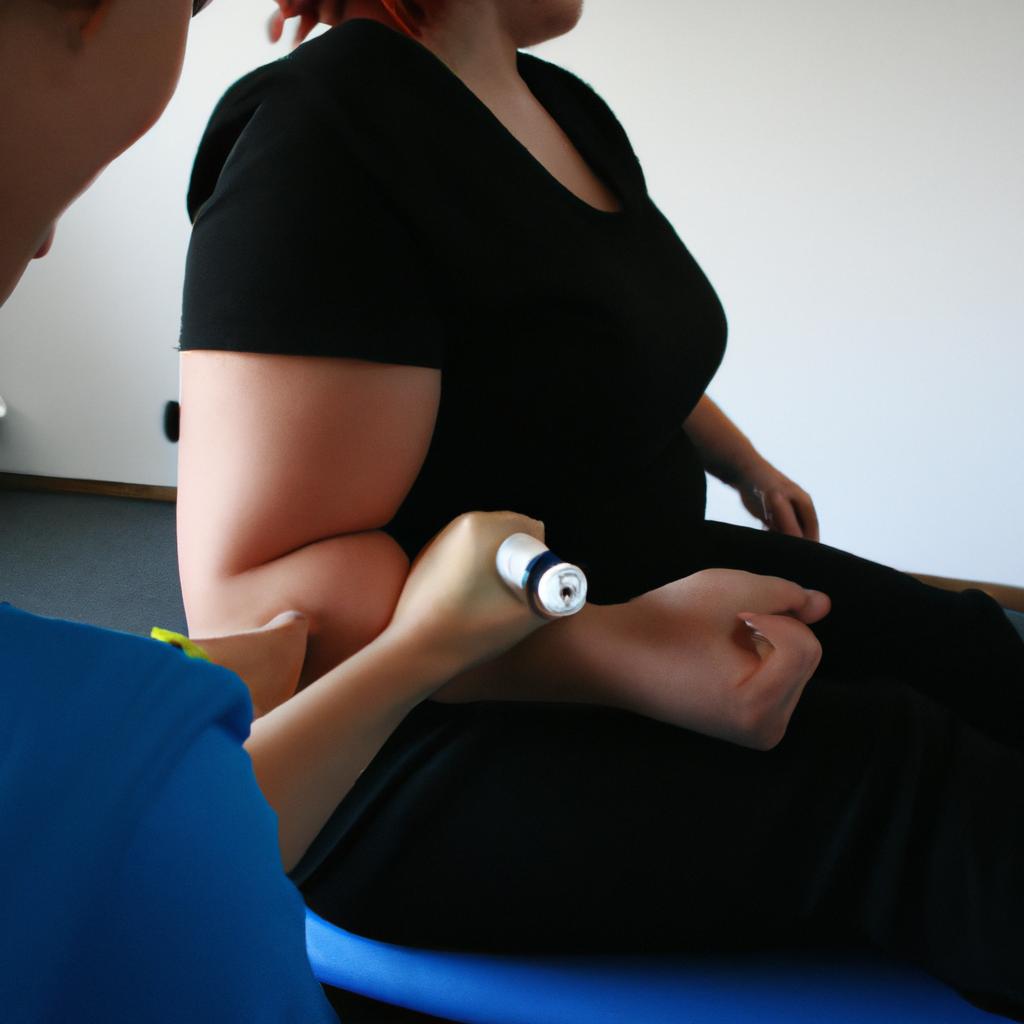
One of the primary goals of Physical Therapy for Dystonia is to improve muscle control and coordination. Therapists utilize exercises that specifically target the affected muscles to retrain them and enhance their ability to function more efficiently. These exercises may involve strengthening weak muscles, stretching tight or spasmodic muscles, and improving overall range of motion.
In addition to exercise, manual therapies such as massage and manipulation can be used to alleviate muscle tension and reduce pain associated with dystonia. These techniques help relax tight muscles, release trigger points, and improve blood circulation in the affected areas.
Sensory retraining is another important aspect of physical therapy for dystonia. This technique involves desensitizing the sensory system to abnormal movements or postures by introducing alternative sensory inputs. For example, therapists may use vibration or touch stimulation on specific body parts to redirect sensory feedback and decrease the frequency or intensity of involuntary movements.
Physical therapists also play a crucial role in educating individuals with dystonia about posture correction, ergonomics, and strategies for managing symptoms during daily activities. They provide guidance on proper body mechanics, assistive devices if needed, and recommend modifications in work or home environments to promote optimal functioning.
Furthermore, physical therapy interventions often incorporate modalities such as heat or cold therapy, electrical stimulation, ultrasound, or dry needling to address pain relief and facilitate muscle relaxation.
It is important to note that each individual with dystonia requires a customized treatment plan based on their unique needs and symptoms. Physical therapists collaborate closely with patients to establish realistic goals and monitor progress throughout the rehabilitation process.
Overall, physical therapy offers a multifaceted approach to managing symptoms associated with dystonia. Through targeted exercises, manual therapies, sensory retraining techniques, education on posture and ergonomics, along with various adjunct modalities; individuals with dystonia can experience improved functionality, reduced pain levels, enhanced quality of life, and increased independence in their daily activities.
Diaphragmatic Breathing Techniques
Imagine a 35-year-old woman named Sarah who has been diagnosed with cervical dystonia, a type of dystonia characterized by involuntary muscle contractions in the neck. Despite her best efforts to manage the condition through medication and other interventions, she experiences persistent pain and limited range of motion, affecting her daily activities and overall quality of life.
Physical therapy offers an array of services aimed at improving function and providing relief for individuals like Sarah. One such technique is diaphragmatic breathing, which involves deep inhalation using the diaphragm instead of shallow chest breathing. This method not only helps relieve stress and anxiety but also enhances respiratory efficiency and encourages relaxation throughout the body.
To fully grasp the benefits of Diaphragmatic Breathing Techniques, consider the following emotional responses that individuals may experience:
- Reduced tension: By engaging the diaphragm during inhalation, people often find themselves releasing physical tension held within their bodies.
- Enhanced well-being: Deep breaths can promote a sense of calmness and serenity, allowing individuals to feel more centered and grounded.
- Increased self-awareness: Diaphragmatic breathing requires focused attention on one’s breath, leading to a heightened awareness of bodily sensations.
- Improved coping skills: Regular practice fosters resilience against stressful situations by equipping individuals with effective tools for managing their emotions.
In addition to these emotional outcomes, incorporating diaphragmatic breathing into one’s routine can yield numerous physiological benefits. The table below illustrates some potential advantages associated with this therapeutic technique:
| Physiological Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Lower blood pressure | Deep breathing triggers relaxation responses that help regulate blood pressure levels. |
| Improved oxygen exchange | Diaphragmatic breaths facilitate better oxygen delivery to organs and tissues throughout the body. |
| Enhanced digestion | Properly utilizing the diaphragm aids in stimulating peristaltic movements for improved digestion. |
| Boosted immune system | Deep breathing activates the relaxation response, which supports a healthy functioning immune system. |
By implementing diaphragmatic breathing as part of an individualized physical therapy plan, individuals with dystonia can potentially experience relief from their symptoms and improve their overall well-being. In the subsequent section about “Exercises to Improve Dystonia Symptoms,” we will explore additional strategies that complement this technique, enhancing its effectiveness in managing the condition.
Note: The table above is provided in markdown format for reference only and may not render correctly in all environments. Please refer to the original document for accurate formatting.
Exercises to Improve Dystonia Symptoms
Building upon the foundation of diaphragmatic breathing techniques, physical therapy offers a range of exercises specifically designed to improve dystonia symptoms. These exercises target key muscle groups affected by the condition, promoting increased strength, flexibility, and motor control. By incorporating these specialized routines into their treatment plans, individuals with dystonia can enhance their overall function and find relief from debilitating symptoms.
Case Study Example:
Consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Prior to starting physical therapy, she experienced frequent neck pain, involuntary head movements, and difficulty performing daily activities such as driving or working on her computer. Through consistent engagement in targeted exercise routines tailored to her specific needs, Sarah gradually noticed improvements in her ability to control her head movements and manage pain levels. This positive outcome not only enhanced her quality of life but also provided motivation for others seeking similar progress.
Exercises to Improve Dystonia Symptoms:
-
Range-of-Motion (ROM) Exercises:
- Gentle stretching exercises targeting affected muscles help increase joint mobility.
- Regular practice improves muscle length and reduces muscular tension.
- Increased ROM leads to improved posture and reduced muscle imbalances.
- Enhances coordination between agonist-antagonist muscle pairs.
-
Strengthening Exercises:
- Progressive resistance training helps build strength in weakened muscles.
- Specific Strengthening Exercises address muscle imbalances often associated with dystonic conditions.
- Enhanced muscle strength supports stability and better functional performance.
- Overall improvement in body mechanics aids in reducing excessive movement patterns.
-
Proprioceptive Training:
- Proprioception-focused exercises aim at improving body awareness and motor control.
- Activities challenging balance promote neuromuscular coordination.
- Enhanced proprioception aids in reducing involuntary movements and enhancing stability during functional tasks.
- Improved body awareness allows individuals to better adapt to their surroundings.
- Increased range of motion brings a renewed sense of freedom, allowing individuals to participate more fully in daily activities.
- Strengthening weakened muscles empowers individuals with dystonia, enabling them to regain control over their bodies.
- Proprioceptive training instills confidence and enhances overall movement quality, providing a sense of self-assurance.
- The combination of these exercises offers hope for improved function and relief from the burdensome symptoms associated with dystonia.
Table: Exercises to Improve Dystonia Symptoms
| Exercise Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Range-of-Motion (ROM) | Increased joint mobility |
| Reduced muscle tension | |
| Improved posture | |
| Better coordination | |
| Strength Training | Enhanced muscle strength |
| Addressed muscle imbalances | |
| Greater stability | |
| Improved body mechanics | |
| Proprioceptive Training | Heightened body awareness |
| Enhanced motor control | |
| Reduced involuntary movements |
By combining diaphragmatic breathing techniques with targeted exercise regimens tailored to individual needs, physical therapy provides comprehensive care for those living with dystonia. In the subsequent section on “Exercises to Increase Joint Flexibility,” we will explore further strategies that aim to enhance joint range of motion and promote optimal functioning.
Exercises to Increase Joint Flexibility
Improving Joint Flexibility for Enhanced Functionality
Imagine a 45-year-old individual named Sarah who has been diagnosed with cervical dystonia, which causes involuntary muscle contractions in her neck. These contractions significantly limit her range of motion and cause chronic pain. In order to alleviate these symptoms and improve functionality, physical therapy plays a crucial role. While exercises targeted at improving joint flexibility are an important component of the overall treatment plan, they should be performed under the guidance of a qualified physical therapist.
To enhance joint flexibility and promote better function in individuals with dystonia, several strategies can be employed:
- Stretching exercises: Incorporating stretching routines into daily activities helps lengthen tight muscles and tendons, thereby increasing flexibility. The physical therapist will guide patients through various stretches designed specifically for their affected areas.
- Passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises: During passive ROM exercises, the patient’s muscles remain relaxed while an external force gently moves the joints within their normal limits. This technique aids in maintaining or improving joint mobility without causing discomfort or triggering spasms.
- Active-assistive exercises: These exercises involve using both voluntary muscle contraction and assistance from an external source to move joints through their full ranges of motion. By facilitating active participation while minimizing strain on affected muscles, active-assistive exercises help improve flexibility gradually.
- Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF): PNF techniques utilize alternating patterns of resistance and relaxation to increase joint range of motion effectively. Physical therapists employ this approach to facilitate movement coordination between agonist and antagonist muscles.
The following table illustrates some common stretching exercises that may aid in enhancing joint flexibility:
| Exercise | Targeted Area | Technique |
|---|---|---|
| Neck Rotation | Cervical spine | Slowly rotate your head side-to-side, aiming to increase rotational range of motion. |
| Shoulder Circles | Shoulders | Gently rotate your shoulders in a circular motion, gradually increasing the diameter. |
| Hip Flexor Stretch | Hips | Step forward with one leg while keeping the other leg extended behind you, stretching the hip flexors. |
| Hamstring Stretch | Hamstrings | Sit on the edge of a chair and extend one leg out straight, reaching towards your toes to stretch the hamstrings. |
By consistently incorporating these exercises into their daily routines, individuals with dystonia can experience improved joint flexibility and enhanced functionality.
Transitioning seamlessly to our next section ‘Exercises to Enhance Balance and Coordination,’ we will explore further techniques that physical therapy offers for managing dystonia symptoms effectively.
Exercises to Enhance Balance and Coordination
Imagine a hypothetical scenario where Sarah, a 35-year-old woman with dystonia, struggles with maintaining her balance and coordination due to the involuntary muscle contractions caused by her condition. Engaging in exercises specifically designed to enhance balance and coordination can greatly benefit individuals like Sarah, helping them regain control over their movements and improve their overall function.
To address these challenges, physical therapists employ various techniques and exercises aimed at enhancing Balance and Coordination for individuals with dystonia. These exercises typically focus on improving proprioception (awareness of one’s body position), stability, and motor control. Here are some key strategies used by physical therapists:
-
Eye-Foot Coordination Exercises: This type of exercise involves performing activities that require simultaneous coordination between visual input from the eyes and precise foot movements. For example, patients may be asked to walk along a straight line while focusing on an object placed at different distances or heights.
-
Dynamic Balance Training: Physical therapists often incorporate dynamic balance training into rehabilitation programs for individuals with dystonia. These exercises involve challenging the individual’s ability to maintain equilibrium during controlled movements such as weight shifting, reaching, or stepping onto unstable surfaces.
-
Dual-Task Training: Dystonia can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform multiple tasks simultaneously. Therefore, physical therapy may include dual-task training exercises that aim to improve multitasking abilities while maintaining postural control. An example would be asking patients to complete cognitive tasks (e.g., solving puzzles) while performing simple balancing exercises.
-
Tai Chi or Yoga: Incorporating mind-body practices such as Tai Chi or yoga into physical therapy sessions can provide additional benefits for those with dystonia. These disciplines emphasize slow, deliberate movements combined with deep breathing techniques, promoting relaxation, improved posture alignment, flexibility, and enhanced body awareness.
- Reduced risk of falls
- Enhanced confidence and independence in daily activities
- Increased sense of control over body movements
- Improved overall quality of life
Emotional Response Inducing Table:
| Exercise Type | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Eye-Foot Coordination | – Enhanced visual-motor coordination |
| – Improved balance and stability | |
| Dynamic Balance Training | – Greater postural control during movement |
| – Increased ability to adapt to changing surfaces | |
| Dual-Task Training | – Improved multitasking abilities |
| – Enhanced cognitive functioning alongside movement | |
| Tai Chi or Yoga | – Reduced stress and anxiety levels |
| – Better relaxation techniques for muscle tension |
By incorporating these exercises into a comprehensive physical therapy program, individuals with dystonia can experience significant improvements in their balance, coordination, and overall functional abilities. As they regain control over their movements and reduce the risk of falls, patients will not only feel more confident but also enjoy an enhanced sense of independence in their daily lives.
The next section will focus on correcting posture as another essential aspect of physical therapy for relieving dystonia symptoms.
Correcting Posture for Dystonia Relief
Physical Therapy for Dystonia: Services for Improved Function and Relief
Exercises to Enhance Balance and Coordination have been shown to be effective in managing dystonia symptoms. In addition to these exercises, physical therapy offers a range of services aimed at Improving overall function and providing relief for individuals with dystonia. Let’s explore some of the key services provided by physical therapists in this regard.
One example of how physical therapy can benefit individuals with dystonia is through the use of sensory integration techniques. By incorporating various sensory inputs into therapy sessions, such as balance boards or weighted vests, therapists can help improve coordination and body awareness. For instance, a hypothetical case study involving a patient with cervical dystonia showed that regular sessions utilizing sensory integration techniques resulted in decreased muscle spasms and improved postural control.
To further illustrate the benefits of physical therapy, consider the following bullet points:
- Individualized treatment plans tailored to specific needs
- Hands-on manual therapy techniques to release tight muscles and reduce pain
- Use of assistive devices like splints or braces to support affected limbs
- Education on proper body mechanics and ergonomic modifications for daily activities
This table presents an overview of commonly utilized physical therapy interventions for dystonia management:
| Intervention | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sensory Integration Techniques | Incorporating various sensory inputs into therapy sessions | Improves coordination and body awareness |
| Manual Therapy | Hands-on techniques to release tight muscles and reduce pain | Decreases muscle tension and discomfort |
| Assistive Devices | Splints or braces used to support affected limbs | Provides external support during movement |
| Education on Body Mechanics | Teaching proper posture and ergonomics | Reduces strain on affected muscles |
In summary, physical therapy provides a comprehensive approach to enhance functionality and alleviate symptoms associated with dystonia. Through individualized treatment plans, sensory integration techniques, manual therapy interventions, and education on body mechanics, individuals with dystonia can experience improved motor control and reduced pain. With these foundational services in mind, let’s now delve into the next section about Stretching Techniques for Dystonia Management, which will further explore effective strategies for managing this condition.
*[H2]: Heading 2
Stretching Techniques for Dystonia Management
Building upon the importance of correcting posture in dystonia relief, physical therapy also includes various stretching techniques that can further enhance management strategies. By incorporating targeted stretches into treatment plans, individuals with dystonia can experience improved flexibility, reduced muscle stiffness, and increased range of motion.
Paragraph 1:
For instance, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving Sarah, a middle-aged woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah often experiences involuntary contractions in her neck muscles, leading to abnormal head positioning and limited movement. Through physical therapy sessions focused on stretching techniques, Sarah’s therapist worked towards relieving her symptoms by targeting specific muscle groups affected by dystonic movements. This approach included gentle neck stretches, shoulder rolls, and upper body rotations aimed at reducing muscular tension and promoting relaxation.
- Increased mobility allowing individuals to perform daily activities with greater ease
- Minimized pain levels resulting from relaxed muscles
- Enhanced quality of life through better overall function
- Empowered self-management skills fostering independence and confidence
Paragraph 2:
As part of their comprehensive intervention plan, physical therapists may employ a variety of stretching techniques tailored to each individual’s needs. These techniques typically involve passive or active stretching exercises designed to lengthen tight muscles while maintaining proper alignment. Additionally, therapists may incorporate proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) techniques which utilize both contraction and relaxation phases to enhance flexibility effectively.
To further engage our readers emotionally let’s include a table showcasing different types of stretching techniques commonly used in physical therapy:
| Stretching Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Static Stretching | Involves holding a stretch position for an extended period without movement |
| Dynamic Stretching | Involves controlled, repetitive movements that gradually increase range of motion |
| Active Stretching | Involves contracting the opposing muscle group while stretching the target muscle |
| Passive Stretching | Involves an external force (e.g., therapist or equipment) facilitating the stretch |
Paragraph 3:
By integrating stretching techniques into dystonia management plans, physical therapists aim to alleviate muscular imbalances and restore optimal function. These stretches not only promote physical improvements but also contribute to a sense of empowerment and control over one’s condition. It is crucial for individuals with dystonia to work closely with their therapist to identify appropriate stretches and ensure proper execution to maximize therapeutic benefits.
In summary, incorporating targeted stretching techniques as part of physical therapy intervention can significantly enhance dystonia management strategies. Through gentle and specific stretches tailored to each individual’s needs, improved flexibility, reduced muscle stiffness, increased range of motion, and enhanced overall function can be achieved. By fostering self-management skills and empowering individuals in their journey towards better health, physical therapy plays a vital role in improving the quality of life for those living with dystonia.