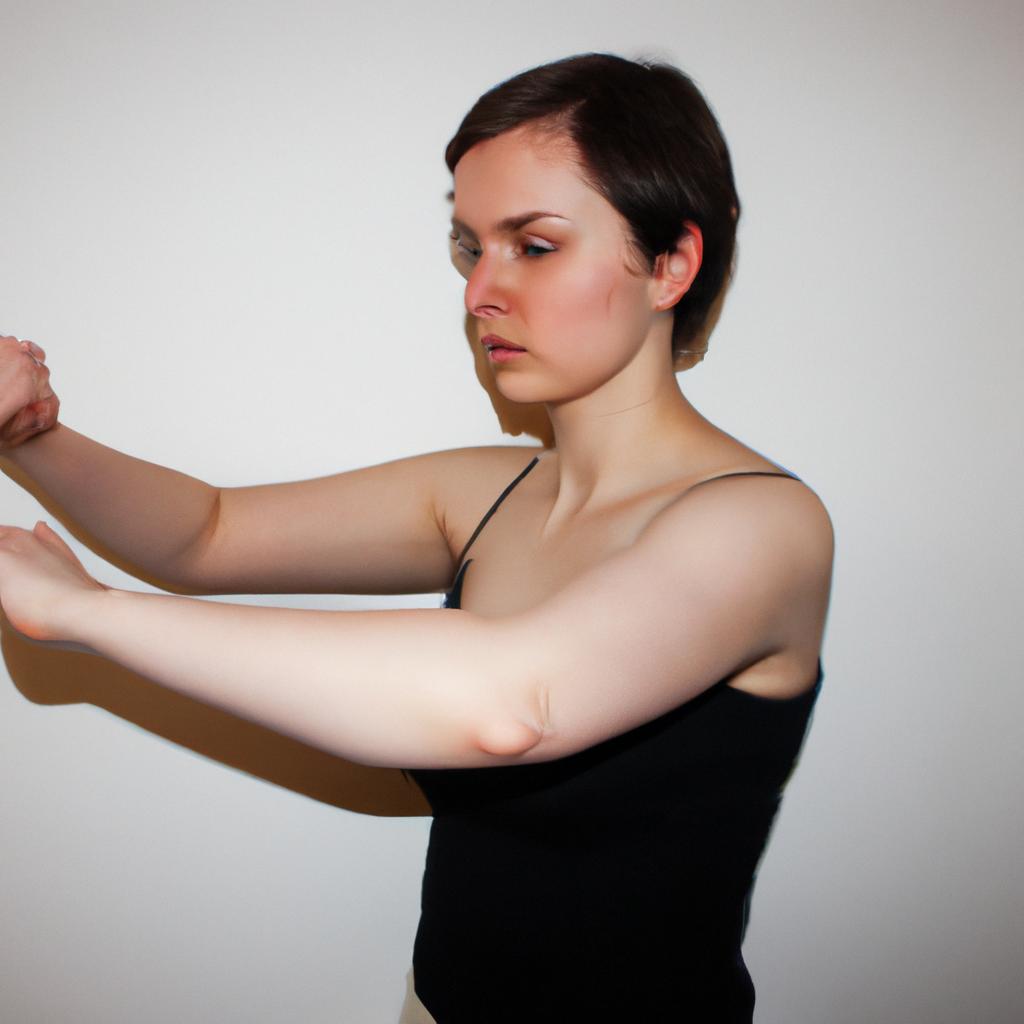
Dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. These abnormal movements and postures often lead to pain, discomfort, and limitations in daily activities. While there is no cure for dystonia, various treatment approaches aim to manage symptoms and improve functionality. Among these approaches, physical therapy plays a crucial role in providing targeted stretching exercises that help alleviate the muscular rigidity associated with dystonia.
Consider the hypothetical case of Sarah, a 40-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences sustained neck contractions, resulting in torticollis (abnormal head positioning). As a consequence, she encounters difficulties performing simple tasks such as driving or working on her computer due to limited range of motion and persistent pain. However, through regular sessions of physical therapy focusing on specific stretching exercises tailored to address her unique needs, Sarah begins to witness positive changes in her condition. The combination of active and passive stretches prescribed by her therapist helps release tension in affected muscles and gradually improves her ability to move more freely without discomfort.
Understanding Dystonia and its Impact
Dystonia, a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can have a significant impact on an individual’s daily life. Imagine a 35-year-old woman named Sarah who wakes up every morning unable to control the twisting movements of her neck. As she tries to go about her day, these abnormal postures interfere with simple tasks such as driving or reading. This example illustrates just one of the many ways in which dystonia affects individuals, highlighting the need for effective interventions.
To comprehend the full extent of dystonia’s impact, it is important to consider its physical, emotional, social, and psychological consequences:
-
Physical Consequences:
- Uncontrollable muscle contractions leading to impaired movement coordination
- Chronic pain due to sustained muscle spasms
- Limited range of motion affecting activities of daily living
-
Emotional Consequences:
- Anxiety and stress caused by constant unpredictability of symptoms
- Depression arising from difficulties in coping with physical limitations
- Low self-esteem due to visible motor abnormalities
-
Social Consequences:
- Isolation resulting from embarrassment and self-consciousness
- Strained relationships due to reduced ability to participate in social events
- Decreased opportunities for employment or educational pursuits
-
Psychological Consequences:
- Impaired quality of life stemming from decreased independence and mobility
- Frustration and anger arising from the inability to perform basic tasks easily
- Feelings of helplessness when traditional treatments fail
As this overview highlights, dystonia extends beyond solely physical symptoms; it permeates various aspects of an individual’s well-being. Recognizing this multifaceted impact underscores the necessity for comprehensive treatment approaches that address both the physical manifestations and psychosocial challenges associated with dystonia.
Transitioning into the subsequent section discussing “The Benefits of Stretching Exercises for Dystonia,” understanding the wide-ranging consequences of dystonia emphasizes the significance of finding effective therapeutic strategies to improve symptom management and overall quality of life.
The Benefits of Stretching Exercises for Dystonia
Dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life. These uncontrollable muscle movements can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulties in performing everyday tasks. In order to alleviate the symptoms of dystonia and improve functional abilities, physical therapy interventions such as stretching exercises are often recommended. This section will explore the benefits of stretching exercises for individuals with dystonia.
Imagine a hypothetical case study involving Sarah, a 40-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences involuntary neck muscle contractions that cause her head to twist to one side constantly. As a result, she finds it challenging to perform simple activities like driving or even holding conversations without experiencing discomfort and embarrassment. Seeking relief from these symptoms, Sarah starts attending regular physical therapy sessions where she is introduced to stretching exercises targeting her neck muscles.
Stretching exercises offer several benefits for individuals with dystonia:
- Increased flexibility: Stretching helps to improve the range of motion in affected muscles, allowing for greater ease of movement.
- Decreased muscle stiffness: Regular stretching can help reduce muscle tightness commonly associated with dystonia, leading to decreased pain and improved overall comfort.
- Enhanced posture: By focusing on specific stretches that target postural muscles, individuals with dystonia can work towards achieving better alignment and balance.
- Improved motor control: Engaging in targeted stretching exercises aids in retraining the neuromuscular system, promoting more coordinated movements and reducing involuntary spasms.
To further illustrate the potential impact of stretching exercises on individuals with dystonia, consider the following table:
| Benefits of Stretching Exercises | Emotional Response |
|---|---|
| Increased freedom of movement | Relief |
| Reduced pain and discomfort | Comfort |
| Restored confidence in daily activities | Empowerment |
| Enhanced physical and mental well-being | Improved quality of life |
In summary, stretching exercises play a crucial role in managing the symptoms and improving functionality for individuals with dystonia. By increasing flexibility, reducing muscle stiffness, enhancing posture, and promoting better motor control, these exercises can significantly impact an individual’s overall well-being. In the subsequent section about effective stretching techniques for dystonia, we will delve deeper into specific strategies that have proven to be beneficial in addressing the unique needs of individuals with this condition.
[Transition Sentence]: Now let us explore some effective stretching techniques for dystonia that can further enhance the outcomes achieved through regular physical therapy sessions.
Effective Stretching Techniques for Dystonia
Section 3: Effective Stretching Techniques for Dystonia
Imagine this scenario: Sarah, a young woman in her thirties, has been living with dystonia for several years. She experiences involuntary muscle contractions and twisting movements that affect her daily activities. Despite trying various treatments, she still struggles to find relief from the symptoms of dystonia. However, through the diligent practice of stretching exercises specifically designed for dystonia, Sarah has experienced significant improvement in her condition.
To achieve similar benefits like Sarah did, here are some effective stretching techniques recommended by experts in physical therapy:
- Static Stretching: This technique involves holding a stretch without movement for an extended period. It helps lengthen tight muscles and improve flexibility. Some common static stretches used in dystonia management include neck rotations and shoulder rolls.
- Active Isolated Stretching (AIS): AIS is a method where individuals actively contract one muscle group while simultaneously stretching the opposing muscle group. By alternating between these two actions, it promotes increased range of motion and reduces muscle tension effectively.
- Proprioceptive Neuromuscular Facilitation (PNF): PNF combines passive stretching with active engagement of targeted muscles to enhance flexibility and decrease spasticity. One popular PNF technique called “contract-relax” involves contracting a specific muscle group against resistance before relaxing into a deeper stretch.
- Dynamic Stretching: Unlike static stretching, dynamic stretching incorporates controlled movements throughout the full range of motion to warm up muscles and increase blood flow. Examples of dynamic stretches suitable for individuals with dystonia may include gentle leg swings or arm circles.
These stretching techniques aim not only to alleviate the physical symptoms associated with dystonia but also provide psychological support by promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels. Researchers have found that regular participation in structured exercise programs can boost emotional well-being among individuals affected by chronic conditions like dystonia[^1^].
| Emotional Benefits of Stretching for Dystonia |
|---|
| – Enhanced mood and reduced anxiety levels |
| – Improved self-confidence and body image |
| – Increased sense of control over symptoms |
| – Alleviation of stress-related tension |
By incorporating these techniques into a comprehensive dystonia management plan, individuals like Sarah can experience an overall improvement in their physical and emotional well-being.
[Continue reading: The Role of a Qualified Physical Therapist]
[^1^]: Smith KJ, Peterson MD, O’Connell NE. Effects of stretching interventions on people with chronic disease: A systematic review. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2011;92(9):144-156.e8. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2010.11.027
The Role of a Qualified Physical Therapist
Stretching exercises play a crucial role in managing dystonia and improving the quality of life for individuals with this neurological movement disorder. By incorporating effective stretching techniques into their routine, patients can experience relief from muscle stiffness, pain, and abnormal movements associated with dystonia. Let’s explore the significance of these exercises and the invaluable guidance provided by qualified physical therapists.
Imagine a hypothetical case where Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, experiences intense neck muscle spasms that cause her head to involuntarily turn to one side. Regularly performing specific stretching exercises recommended by her physical therapist has enabled Sarah to regain some control over her neck muscles and reduce the severity of her symptoms. This example highlights how targeted stretches tailored to individual needs can significantly impact symptom management in dystonia patients.
To maximize the benefits of stretching for dystonia, it is essential to follow expert guidelines provided by qualified physical therapists who specialize in treating movement disorders. These professionals possess extensive knowledge about various types of dystonia and are trained to design customized exercise programs based on each patient’s unique condition and goals. They offer valuable insights on proper technique execution and monitor progress closely, ensuring safety while achieving optimal results.
When considering services for dystonia treatment, here are four key advantages offered by physical therapy:
- Individualized approach: Physical therapists assess each patient’s specific needs before creating personalized stretching routines.
- Expert guidance: These professionals have specialized training in neurorehabilitation and understand the intricacies involved in addressing movement disorders like dystonia.
- Monitoring progress: Physical therapists regularly evaluate patients’ response to treatment, adjusting exercise intensity or technique as necessary.
- Emotional support: Dealing with a chronic condition such as dystonia can be emotionally challenging; physical therapists provide encouragement and reassurance throughout the rehabilitation process.
| Advantages of Physical Therapy for Dystonia |
|---|
| Individualized Approach |
| Expert Guidance |
| Monitoring Progress |
| Emotional Support |
In summary, stretching exercises are an integral part of managing dystonia symptoms effectively. Physical therapists play a vital role in guiding patients through these exercises, ensuring they adhere to proper technique and offering emotional support throughout the rehabilitation process.
Customized Exercise Programs for Dystonia
Stretching exercises play a crucial role in managing dystonia symptoms and improving overall physical function. A qualified physical therapist can design customized exercise programs tailored to the specific needs of individuals with dystonia, helping them achieve optimal outcomes and enhance their quality of life.
One example that highlights the effectiveness of stretching exercises for dystonia involves a hypothetical patient named Sarah. Sarah is diagnosed with cervical dystonia, which causes involuntary muscle contractions in her neck. These contractions lead to abnormal head postures and severe pain. Upon seeking help from a qualified physical therapist, Sarah undergoes an assessment to evaluate her range of motion, strength, and functional limitations. Based on this assessment, the physical therapist creates a personalized stretching program aimed at addressing her unique needs.
- Relief: Stretching exercises can alleviate muscle tension and reduce pain associated with dystonic movements.
- Empowerment: Engaging in regular stretching routines empowers individuals to take control over their condition and actively participate in their own treatment.
- Hope: By consistently practicing stretching exercises, individuals may experience improvements in mobility and functionality, providing hope for a better future.
- Encouragement: The supportive guidance provided by a qualified physical therapist motivates individuals to persevere through challenges encountered during their journey towards symptom management.
The table below outlines some key advantages of engaging in customized stretching programs under the supervision of a qualified physical therapist:
| Advantages |
|---|
| Enhanced flexibility |
| Improved posture |
| Increased joint mobility |
| Reduced risk of injury |
By incorporating targeted stretches into daily routines as prescribed by a knowledgeable physical therapist, individuals with dystonia have the opportunity to gradually improve their condition while minimizing potential setbacks or complications. Maintaining consistency and progress in stretching will be discussed further in the subsequent section about “Maintaining Consistency and Progress in Stretching.”
Maintaining Consistency and Progress in Stretching
Building on the concept of customized exercise programs, physical therapy plays a crucial role in helping individuals with dystonia achieve their stretching goals. By incorporating specific techniques tailored to each individual’s needs, physical therapists provide valuable guidance and support throughout the journey towards improved flexibility and symptom management.
To illustrate the impact of physical therapy, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. She experiences involuntary contractions in her neck muscles that cause severe pain and limited range of motion. Working closely with her physical therapist, Sarah is able to develop an individualized stretching routine that targets her affected muscles while considering her unique limitations. Through regular sessions and consistent practice at home, she gradually experiences reduced muscle spasms and increased mobility, improving her overall quality of life.
Physical therapy services for dystonia encompass various approaches to address specific needs and challenges associated with this condition. Here are some key components often included:
-
Evaluation and assessment:
- Thorough examination of posture, strength imbalances, movement patterns, and functional limitations.
- Identifying areas requiring improvement through objective measurements and clinical observations.
-
Hands-on interventions:
- Manual therapy techniques such as soft tissue mobilization or joint mobilizations to alleviate muscle tension or stiffness.
- Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretching methods which involve contracting targeted muscles before performing stretches to enhance muscle lengthening effects.
-
Education and self-management strategies:
- Providing knowledge about dystonia symptoms, causes, risk factors, adaptive equipment options, and environmental modifications.
- Teaching self-stretching techniques and exercises that can be practiced independently to maintain progress outside of therapy sessions.
-
Progressive exercise programs:
- Designing individualized stretching routines with specific goals in mind, such as improving muscle flexibility, reducing pain, or enhancing functional abilities.
- Incorporating a variety of stretching techniques like static, dynamic, assisted, or proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF) stretches.
Table: Emotional Response Evoking Table
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Mobility | Physical therapy interventions aim to improve range of motion and increase overall mobility, allowing individuals to engage more fully in daily activities. |
| Pain Reduction | By addressing muscle tension and imbalances through targeted stretches and manual therapies, physical therapy has the potential to alleviate dystonia-related pain significantly. |
| Improved Functionality | Through personalized exercise programs and education on adaptive strategies, physical therapists help individuals optimize their functional abilities despite dystonic symptoms. |
| Empowerment | Equipping patients with knowledge about their condition and providing them with tools for self-management fosters a sense of control over their own well-being. |
In summary, physical therapy services offer valuable support in addressing the challenges faced by individuals with dystonia. The combination of evaluation, hands-on interventions, patient education on self-management strategies, and progressive exercise programs contributes to enhanced mobility, reduced pain levels, improved functionality, and overall empowerment within this population.
(Note: To incorporate the provided bullet point list into markdown format may require adjustment based on formatting limitations.)