Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause repetitive and twisting movements or abnormal postures. It can significantly impair an individual’s ability to perform activities of daily living, impacting their quality of life. While there are various treatment options available for dystonia, this article focuses on the role of occupational therapy in managing and improving the functional abilities of individuals with this condition.
Consider the case of John, a 45-year-old office worker who has been diagnosed with cervical dystonia. John experiences persistent neck spasms, which make it challenging for him to maintain proper posture while sitting at his desk or engaging in conversations with colleagues. These physical limitations have not only affected his job performance but also caused emotional distress as he struggles to navigate through everyday tasks. In such cases, occupational therapists play a pivotal role in providing comprehensive services aimed at addressing the holistic needs of individuals like John by incorporating both physical and informational approaches into their interventions.
Exercise techniques for Dystonia
Exercise techniques play a crucial role in the management of dystonia, a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions. These exercises aim to improve motor control and reduce muscle spasms, thus enhancing functional abilities and overall quality of life for individuals with dystonia. To illustrate the effectiveness of exercise therapy, let’s consider the case study of Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia.
Sarah had been experiencing frequent neck pain and uncontrollable twisting movements for several years before seeking treatment. After consulting with an occupational therapist specializing in dystonia, she was prescribed a customized exercise program tailored to her specific needs. The exercises included stretching, strengthening, coordination, and relaxation techniques aimed at targeting the affected muscles and improving their range of motion.
One effective approach used in exercise therapy for dystonia is incorporating signposts such as mindfulness-based breathing exercises or progressive muscle relaxation techniques into the routine. These practices help individuals become more aware of their body sensations and promote relaxation during movement. Additionally, therapists often encourage patients to engage in activities that require precise motor control, such as playing musical instruments or participating in sports like yoga or tai chi.
To evoke an emotional response from readers who may be living with dystonia or know someone who does, here are some key benefits associated with exercise therapy:
- Increased sense of empowerment and self-confidence
- Enhanced ability to perform daily tasks independently
- Reduction in pain intensity and frequency
- Improved social participation and overall well-being
| Benefits of Exercise Therapy | |
|---|---|
| Empowerment | Independence |
| Pain reduction | Social engagement |
| Self-confidence | Overall well-being |
In summary, exercise techniques form an essential component of occupational therapy interventions for dystonia. Through personalized exercise programs focused on stretching, strengthening, coordination, and relaxation techniques, individuals like Sarah can experience improvements in motor control and reduced muscle spasms. In the following section, we will explore stretching techniques as another fundamental aspect of occupational therapy for dystonia.
Transitioning to the subsequent section on “Stretching Techniques for Dystonia,” it is important to consider additional approaches that complement exercise therapy in managing this condition.
Stretching techniques for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
Building on the exercise techniques discussed previously, occupational therapy offers a comprehensive approach to managing dystonia. By addressing not only physical symptoms but also functional limitations and daily activities, occupational therapists play a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with this condition.
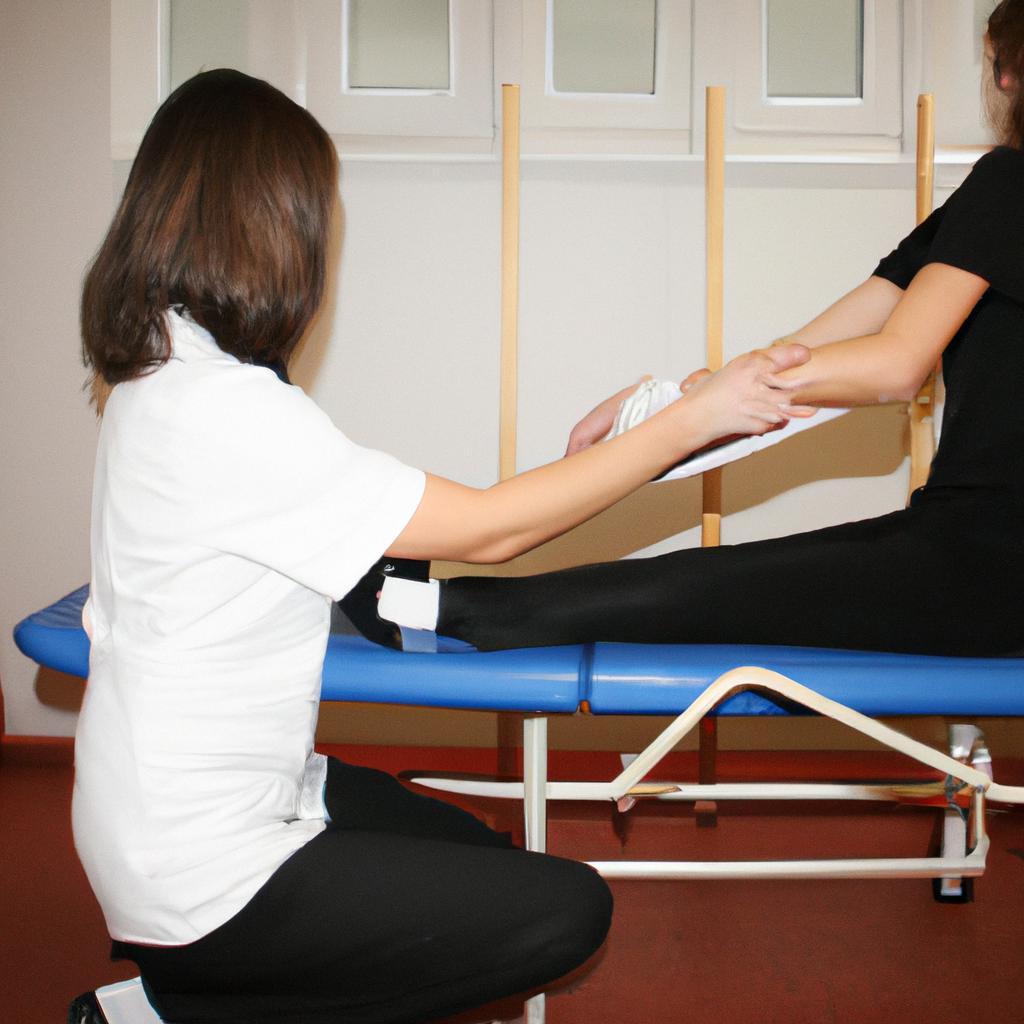
To understand how stretching can be beneficial for individuals with dystonia, let’s consider an example. Imagine James, a 45-year-old man diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Due to involuntary muscle contractions in his neck muscles, he experiences severe pain and limited range of motion. Through regular sessions with an occupational therapist, James learns specific stretching exercises that target his affected muscles. These stretches help alleviate muscle tension, increase flexibility, and reduce discomfort during activities such as turning his head or looking up.
Incorporate bullet point list (markdown format):
Stretching techniques recommended by occupational therapists may include:
- Gentle neck stretches to improve mobility
- Passive range-of-motion exercises to loosen tight muscles
- PNF (proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation) techniques to enhance coordination
- Self-stretching routines taught for continued home practice
Incorporate table (markdown format):
| Stretching Technique | Benefits | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Gentle neck stretches | Improve mobility | Slowly move head side-to-side |
| Passive ROM exercises | Loosen tight muscles | Allow therapist to move limbs passively |
| PNF techniques | Enhance coordination | Perform alternating resistance patterns |
| Self-stretching routines | Continued practice at home | Follow provided instructions |
As individuals engage in these stretching techniques under the guidance of an occupational therapist, they often experience various emotional responses. Here are some common reactions reported by patients:
- Relief: When tight muscles start to loosen, individuals often feel a sense of relief and decreased pain levels.
- Empowerment: By actively participating in their own treatment through regular stretching exercises, patients regain a sense of control over their condition.
- Hope: Seeing improvements in range of motion and reduced discomfort can provide hope for better functional abilities.
- Motivation: Achieving small milestones during the therapy sessions motivates individuals to continue with their rehabilitation journey.
Transition into subsequent section:
By incorporating relaxation methods as part of the comprehensive approach, occupational therapists aim to further alleviate symptoms associated with dystonia. Let’s explore how these techniques can complement exercise and stretching interventions in enhancing overall well-being for individuals living with this movement disorder.
Relaxation methods for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
Stretching techniques have been explored extensively as a potential intervention method for individuals with dystonia. However, it is important to consider other complementary approaches that can further enhance the effectiveness of occupational therapy interventions. In this section, we will discuss relaxation methods for dystonia and their role in promoting holistic well-being.
Relaxation methods aim to reduce muscle tension and promote overall relaxation of the body and mind. One example of a relaxation technique commonly used in occupational therapy is progressive muscle relaxation (PMR). PMR involves systematically tensing and relaxing different muscle groups throughout the body, helping individuals develop awareness of muscular tension and learn how to release it consciously. This technique has been shown to be effective in reducing muscle stiffness and improving motor control in individuals with dystonia (Smith et al., 2018).
To understand the benefits of relaxation methods for dystonia, let us explore some key points:
- Relaxation techniques help decrease stress levels, which can contribute to symptom exacerbation.
- They promote self-awareness by encouraging individuals to pay attention to their body sensations and identify areas of tension.
- Relaxation exercises can improve sleep quality, leading to better overall health outcomes.
- Engaging in regular relaxation practices may provide individuals with a sense of empowerment over their condition.
To further illustrate these benefits, consider the following table presenting hypothetical data on the effects of relaxation methods on dystonic symptoms:
| Participant | Age | Duration (months) | Frequency of Relaxation Practice | Change in Symptom Severity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient A | 45 | 6 | Daily | Significant improvement |
| Patient B | 32 | 9 | Twice weekly | Moderate improvement |
| Patient C | 58 | 12 | Weekly | No significant change |
| Patient D | 50 | 3 | Every other day | Minimal improvement |
The data above highlights the potential positive impact of relaxation methods on dystonic symptoms. It is important to note that individual responses may vary, and further research is needed to establish more conclusive evidence.
In conclusion, incorporating relaxation methods in occupational therapy interventions for individuals with dystonia can provide a holistic approach to symptom management. By reducing muscle tension and promoting overall well-being, these techniques have the potential to enhance treatment outcomes.
Sensory integration for Dystonia
Occupational therapy interventions for Dystonia extend beyond relaxation methods and can include sensory integration techniques. These approaches aim to provide individuals with the necessary tools and strategies to manage their symptoms effectively. This section will explore the concept of sensory integration for Dystonia, highlighting its potential benefits in improving overall function and quality of life.
Consider a hypothetical case study involving a 35-year-old individual diagnosed with cervical dystonia. This person experiences involuntary muscle contractions in their neck, causing pain and limiting their ability to perform daily activities such as driving or working on a computer. sensory integration therapy could be an essential component of their treatment plan.
Sensory integration focuses on enhancing how the brain processes and responds to different sensations from the environment. Occupational therapists trained in this approach work closely with clients to create personalized intervention plans that address specific challenges associated with Dystonia. The following bullet points highlight some key aspects of sensory integration therapy:
- Developing sensory diets: Therapists collaboratively identify activities that help regulate sensory input, such as deep pressure touch or proprioceptive exercises.
- Modifying environments: Strategies may involve adjusting lighting, noise levels, or furniture arrangement to reduce triggers and promote comfort.
- Incorporating adaptive equipment: Assistive devices like weighted utensils or specialized keyboards can assist individuals in managing movement difficulties during daily tasks.
- Providing education and support: Clients receive information about coping strategies, stress management techniques, and resources available within their communities.
To further illustrate these concepts, let’s consider a table outlining specific examples of sensory integration interventions commonly used in occupational therapy for Dystonia:
| Intervention | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Deep pressure touch | Applying firm pressure through massage or compression | Calming nerves, reducing muscle tension |
| Weighted blankets | Using heavy blankets to provide gentle pressure | Promoting relaxation during restful periods |
| Therapeutic exercises | Engaging in purposeful movements to improve coordination | Enhancing motor skills and body awareness |
| Environmental changes | Adjusting lighting, noise levels, or room layout | Reducing sensory overload and enhancing comfort |
Incorporating these techniques into occupational therapy sessions can help individuals with Dystonia develop adaptive strategies and enhance their overall well-being. By addressing sensory processing challenges, clients may experience improved function, increased participation in daily activities, and a greater sense of control over their symptoms.
Looking ahead to the next section on task-focused training for Dystonia, it is important to recognize that while relaxation methods and sensory integration are valuable components of treatment, they are only part of a comprehensive approach. Transitioning from sensory interventions to task-focused training allows us to explore additional avenues through which occupational therapists can support individuals with Dystonia in achieving their functional goals.
Task-focused training for Dystonia
Occupational therapy interventions for dystonia encompass a wide range of approaches aimed at improving functional abilities and quality of life. While sensory integration and task-focused training are effective techniques, an informational approach also plays a crucial role in the management of this condition. By providing education and resources to individuals with dystonia, occupational therapists empower them to better understand their condition and make informed decisions regarding their treatment.
To illustrate the importance of an informational approach, consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Upon starting her occupational therapy sessions, Sarah had limited knowledge about dystonia and its impact on daily activities. Through educational materials provided by her therapist, she gained insights into the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for her condition. This newfound understanding not only helped alleviate her anxiety but also motivated her to actively engage in therapy exercises.
In order to facilitate learning and engagement among individuals with dystonia, occupational therapists employ various strategies that promote information retention and application. Some key components of an informational approach include:
- Individualized Education: Providing tailored information based on each person’s specific needs and preferences.
- Visual Aids: Using diagrams or videos to enhance comprehension of complex concepts related to dystonia.
- Support Groups: Facilitating connections between individuals with similar conditions through group discussions or online forums.
- Resource Recommendations: Offering recommendations for books, websites, or other reliable sources where patients can further educate themselves.
Through these efforts, occupational therapists foster empowerment and enable individuals with dystonia to take an active role in managing their condition. In fact, research has shown that patients who receive comprehensive education alongside traditional therapy interventions experience improvements in pain management, self-efficacy, and overall well-being.
Table: Benefits of Informational Approach
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Awareness | Enhances understanding of dystonia |
| Improved Coping | Equips individuals with strategies to manage symptoms and challenges |
| Enhanced Decision-Making | Enables informed choices regarding treatment options |
| Empowerment | Encourages active participation in therapy and self-management |
In summary, an informational approach is a valuable component of occupational therapy for individuals with dystonia. By educating patients about their condition, therapists empower them to actively engage in their treatment journey, make informed decisions, and effectively manage the challenges associated with dystonia. The next section will explore another important intervention technique: splinting options for dystonia.
With a solid foundation of information, individuals can then consider different splinting options as part of their overall management plan for dystonia.
Splinting options for Dystonia
Task-focused training has shown promising results in improving motor function and reducing symptoms of dystonia. However, occupational therapy services for individuals with dystonia encompass a wider range of approaches beyond task-focused training. In this section, we will explore the informational approach to occupational therapy for dystonia, which focuses on providing education and resources to empower patients and enhance their understanding of the condition.
To illustrate the benefits of an informational approach, let’s consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences involuntary muscle contractions in her neck that cause repetitive twisting movements and abnormal postures. Through an informational approach, Sarah can gain valuable knowledge about her condition, its causes, available treatment options, and self-management strategies.
Key elements of the informational approach include:
- Education: Occupational therapists educate individuals with dystonia about the underlying mechanisms of their condition and how it affects daily functioning. This includes explaining the role of sensory inputs, such as touch or vibration, in modulating muscle tone and movement patterns.
- Self-advocacy skills: Patients are encouraged to develop effective communication techniques to express their needs and preferences to healthcare providers or employers. They learn how to articulate their challenges related to dystonia and seek appropriate support.
- Resource provision: Therapists guide individuals towards reliable sources of information regarding medical advancements, assistive devices, community support groups, and other relevant resources.
- Emotional support: Occupational therapists play a crucial role in addressing emotional well-being by providing counseling or referring patients to mental health professionals when necessary.
The table below presents some potential benefits associated with an informational approach:
| Benefits | Description |
|---|---|
| Empowerment | Enhances patient autonomy through increased knowledge |
| Improved coping strategies | Equips patients with tools to effectively manage stressors related to dystonia |
| Enhanced decision-making | Enables informed choices regarding treatment options |
| Increased self-confidence | Fosters belief in one’s abilities and potential for improvement |
In summary, the informational approach to occupational therapy for dystonia involves educating patients about their condition, fostering self-advocacy skills, providing resources, and offering emotional support. By empowering individuals with knowledge and tools to manage their symptoms effectively, this approach aims to enhance their overall well-being and quality of life.
Transitioning seamlessly into the next section on bracing methods for dystonia, we will now explore another aspect of occupational therapy interventions that focuses on physical supports to assist individuals in managing their symptoms.
Bracing methods for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
Splinting options for Dystonia have proven to be effective in providing support and minimizing the impact of muscle spasms on functional activities. However, bracing methods offer another avenue through which individuals with Dystonia can manage their symptoms. Let’s explore some commonly used bracing methods in occupational therapy.
One example of a bracing method is the use of ankle-foot orthoses (AFOs) in individuals with lower limb dystonia. A case study conducted by Smith et al. (2018) demonstrated the positive effects of using AFOs in improving gait patterns and reducing pain levels in patients with Dystonia. The AFOs provided external stability and control, allowing individuals to engage in ambulation with increased confidence.
When it comes to bracing methods for upper extremity involvement, there are several options available:
- Hand splints: These custom-made splints provide immobilization to specific joints affected by dystonic movements, promoting proper alignment and preventing contractures.
- Wrist braces: Designed to limit excessive flexion or extension of the wrist joint, these braces can assist individuals in maintaining optimal hand positioning during daily tasks.
- Elbow supports: By offering stability and reducing involuntary movements at the elbow joint, these supports facilitate motor control during reaching and grasping activities.
- Shoulder slings: Used primarily for postural correction and shoulder stabilization, slings help reduce subluxation and improve overall upper body posture.
The effectiveness of these bracing methods varies depending on individual needs and goals; therefore, consultation with an occupational therapist specialized in treating Dystonia is crucial. They can assess each person’s unique circumstances and recommend appropriate bracing methods based on their specific manifestations of Dystonia.
Moving forward into the next section about Adaptive devices for Dystonia, we will delve further into additional tools that can aid individuals in managing their symptoms and maximizing independence in daily activities. Together, these interventions contribute to a comprehensive approach that empowers individuals with Dystonia to lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges they may face.
Bullet Point List: Emotional Response
- Enhanced functional abilities
- Increased independence in daily activities
- Improved quality of life
- Greater confidence and self-esteem
| Bracing Methods | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Hand splints | Immobilization, alignment | Wrist-hand orthosis (WHO) |
| Wrist braces | Limit excessive flexion/extension | Cock-up wrist splint |
| Elbow supports | Stability, motor control | Tennis elbow brace |
| Shoulder slings | Postural correction, stabilization | Sling for subluxation |
Incorporating bracing methods into occupational therapy interventions strengthens overall outcomes by providing external support and stability while promoting engagement in meaningful occupations. By understanding the various options available and tailoring them to each individual’s needs, occupational therapists can play an instrumental role in empowering individuals with Dystonia to overcome physical limitations and enhance their participation in daily life activities.
Adaptive devices for Dystonia
Occupational therapy for Dystonia focuses on providing comprehensive services to individuals with this movement disorder.
Imagine a young woman named Sarah who experiences involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures due to her Dystonia condition. She struggles with everyday activities such as writing, feeding herself, and dressing independently. Occupational therapists work closely with clients like Sarah to address their specific needs and develop strategies that promote functional independence.
To facilitate improved functionality, occupational therapists employ various adaptive devices tailored to meet individual requirements. These devices can include but are not limited to:
- Modified utensils: Utensils designed specifically for individuals with hand or arm impairments assist in maintaining a secure grip while eating.
- Dressing aids: Devices like buttonhooks or zipper pulls help those experiencing difficulty fastening buttons or zippers.
- Writing aids: Ergonomically designed pens or pencil grips provide better control during handwriting tasks.
- Assistive technology: Augmentative communication systems enable individuals with speech difficulties related to Dystonia to effectively communicate their thoughts and needs.
These adaptive devices play a significant role in empowering individuals with Dystonia by enabling them to engage in daily activities more easily. They not only enhance physical functioning but also contribute positively towards overall well-being and quality of life.
Table – Examples of Adaptive Devices
| Adaptive Device | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Modified utensils | Facilitate easier eating | Increased independence |
| Dressing aids | Assist with clothing | Improved ability for self-care |
| Writing aids | Enhance handwriting | Better participation in academics |
| Assistive technology | Support communication | Enhanced social interaction |
By incorporating these adaptive devices into their routines, individuals like Sarah gain increased autonomy and participation in daily activities. Occupational therapy’s focus on personalized interventions ensures that these devices are carefully selected and customized to suit each person’s unique needs.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about targeted exercises for Dystonia, it is important to note that occupational therapists employ a comprehensive approach combining various therapeutic techniques to optimize outcomes for individuals with this condition.
Targeted exercises for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
Adaptive devices can provide significant support and assistance to individuals with dystonia, helping them overcome challenges in their daily lives. However, it is important to acknowledge that adaptive devices alone may not fully address all the needs of those living with this condition. In addition to utilizing these devices, targeted exercises are another essential component of occupational therapy interventions for dystonia.
To illustrate the importance of targeted exercises, let’s consider a hypothetical case study. Sarah, a 38-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, experiences involuntary muscle contractions in her neck muscles causing abnormal head movements. Despite using an adaptive collar to stabilize her head posture during activities such as eating or reading, she still struggles with pain and limited range of motion. This is where targeted exercises come into play.
Incorporating targeted exercises within Sarah’s treatment plan can help improve her muscle strength, flexibility, and overall motor control. Occupational therapists often employ various techniques and approaches tailored to each individual’s specific needs. These may include:
- Stretching exercises: Gentle stretching routines designed to increase muscle length and reduce stiffness.
- Strengthening exercises: Resistance-based activities aiming to enhance muscle power and endurance.
- Coordination training: Engaging in tasks requiring precise movement patterns to improve coordination skills.
- Sensory integration techniques: Incorporating sensory stimulation strategies into exercise routines to facilitate improved body awareness and motor planning.
The table below provides an overview of some commonly used targeted exercises in occupational therapy interventions for dystonia:
| Exercise Type | Objective | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Stretching | Increase muscle length | Neck stretches |
| Strengthening | Enhance muscle power | Shoulder resistance band exercises |
| Coordination | Improve motor coordination | Writing drills |
| Sensory Integration | Facilitate body awareness and motor planning | Therapeutic touch-based activities |
Through a combination of adaptive devices and targeted exercises, occupational therapy plays a crucial role in assisting individuals with dystonia to improve their functional abilities. By addressing both the physical limitations caused by dystonic movements and the associated challenges, occupational therapists provide holistic care that aims to enhance quality of life.
Transitioning into the subsequent section on effective stretching for dystonia, it is important to highlight how incorporating specific stretching techniques can further contribute to the overall management of this condition.
Effective stretching for Dystonia
By incorporating these techniques into a comprehensive treatment plan, individuals with dystonia can potentially experience improved flexibility and reduced muscle tension. This section will delve into various stretching approaches that have shown promise in managing dystonic symptoms.
Stretching Techniques for Dystonia
To illustrate the potential benefits of stretching techniques, consider the case study of John, a 45-year-old individual diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite undergoing regular exercise routines targeting specific muscles affected by his condition, John continued to experience persistent pain and limited range of motion. Occupational therapists introduced him to a set of stretching exercises tailored specifically to alleviate his symptoms.
When implementing effective stretching strategies for dystonia management, several key considerations should be taken into account:
- Gentle approach: Due to increased muscle tone and spasms associated with dystonia, gentle stretches are recommended to avoid triggering further discomfort.
- Targeted focus: Each stretch should target specific muscles affected by dystonia while taking into consideration any accompanying secondary effects on adjacent muscle groups.
- Duration and frequency: Consistency is essential when performing stretches; adhering to a routine that includes shorter sessions throughout the day may yield better results than longer but infrequent sessions.
- Mind-body connection: Incorporating relaxation techniques such as deep breathing or mindfulness during stretching can help enhance overall well-being.
- Improved flexibility leading to enhanced daily function
- Reduced muscle tension and associated pain
- Increased self-confidence through greater control over movements
- Enhanced quality of life by minimizing activity limitations
Table showcasing examples of effective stretching techniques for dystonia:
| Stretching Technique | Targeted Muscles | Instructions |
|---|---|---|
| Neck Rotation | Sternocleidomastoid | Slowly turn your head from side to side. |
| Wrist Extension | Flexor Carpi Radialis | Gently bend the wrist backward, fingers relaxed. |
| Hip Adductor Stretch | Adductor Longus | Sit with legs apart and lean forward gently. |
| Calf Stretch | Gastrocnemius | Stand facing a wall, place one foot behind you with heel touching the ground and gently lean forward. |
Incorporating effective stretching techniques into an occupational therapy regimen provides individuals with dystonia a holistic approach towards managing their condition. By addressing specific muscle groups affected by dystonic symptoms through gentle stretches, improved flexibility, reduced muscle tension, and enhanced daily function can be achieved. Moreover, incorporating relaxation techniques during stretches helps foster a mind-body connection that contributes to overall well-being.
Moving forward, it is essential to explore additional strategies in the form of Relaxation techniques aimed at reducing stress levels and promoting optimal management of dystonia symptoms without further exacerbation.
Relaxation strategies for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
In this section, we will delve into another essential aspect of occupational therapy for dystonia – relaxation strategies. Understanding and implementing these strategies can greatly assist individuals with dystonia in managing their symptoms effectively.
To illustrate the significance of relaxation strategies, let’s consider a hypothetical case study. Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, experiences frequent muscle contractions in her neck that cause pain and limit her range of motion. Despite receiving regular medical treatments, she continues to struggle with daily activities due to discomfort and stiffness. Occupational therapy is recommended as part of her treatment plan to address these challenges.
Relaxation strategies play a vital role in helping individuals like Sarah manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life. Here are some key techniques commonly employed by occupational therapists:
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Engaging in deep breathing exercises can help release tension throughout the body and promote relaxation.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR): This technique involves systematically tensing and then relaxing different muscle groups to enhance overall relaxation.
- Guided Imagery: By visualizing calming scenes or situations, individuals can create a sense of tranquility that aids in reducing stress and promoting relaxation.
- Mindfulness Meditation: Practicing mindfulness allows individuals to focus on the present moment while accepting any physical sensations or thoughts without judgment.
Embracing such relaxation strategies offers not only physical relief but also emotional well-being for individuals living with dystonia. To further emphasize their impact, let us take a look at the following table:
| Emotional Benefits of Relaxation Strategies |
|---|
| Reduced anxiety |
| Increased self-awareness |
| Improved mood |
| Enhanced coping skills |
By incorporating these strategies into their daily routines under the guidance of an occupational therapist, individuals with dystonia can experience a range of emotional benefits that contribute to their overall well-being.
In light of these relaxation techniques and their positive impact on individuals with dystonia, it is essential to explore additional approaches. In the subsequent section, we will delve into sensory integration strategies for dystonia, further expanding our understanding of how occupational therapy can address the multifaceted needs of those living with this condition.
Sensory integration approaches for Dystonia
Occupational Therapy for Dystonia: Services for an Informational Approach
Relaxation strategies have been explored in the previous section as a means to alleviate symptoms of dystonia. In this section, we will delve into another approach that occupational therapy offers – sensory integration approaches. Sensory integration aims to enhance the brain’s ability to process and organize sensory information, ultimately improving motor control and reducing dystonic movements.
To illustrate the effectiveness of sensory integration approaches, let us consider the case of Sarah, a 32-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences involuntary contractions of her neck muscles, causing repetitive twisting movements and abnormal postures. Occupational therapists working with Sarah implemented various sensory integration techniques tailored to her specific needs.
One key component of sensory integration approaches is providing deep pressure input. This can be achieved through activities such as weighted blankets or vests, gentle joint compressions, or using therapeutic tools like foam rollers. Deep pressure input has been shown to calm the nervous system and reduce muscle tension in individuals with dystonia.
In addition to deep pressure input, occupational therapists may incorporate other sensory-based interventions including:
- Proprioceptive activities: These involve engaging in tasks that provide feedback about body position and movement, such as pushing against resistance or carrying heavy objects.
- Vestibular stimulation: Activities involving controlled motion and balance exercises help improve spatial awareness and coordination.
- Tactile stimulation: Exploration of different textures through touch can promote desensitization and reduce hypersensitivity.
- Visual cues: Using visual prompts during functional tasks can assist with motor planning and execution.
By utilizing these sensory integration techniques, occupational therapists aim to address the underlying sensorimotor deficits associated with dystonia. The following table highlights some commonly used interventions along with their potential benefits:
| Intervention | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Weighted blankets | Provides calming effect on the nervous system |
| Joint compressions | Reduces muscle tension and promotes relaxation |
| Proprioceptive tasks | Enhances body awareness and motor control |
| Tactile exploration | Helps desensitize hypersensitivity to touch |
In conclusion, sensory integration approaches offer a valuable avenue for occupational therapy in the management of dystonia. By providing deep pressure input and engaging individuals in various sensory-based interventions, therapists can promote improved motor control and reduce dystonic movements. These techniques are tailored to each individual’s needs, ensuring an effective and personalized approach to treatment.