Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that result in abnormal postures and repetitive movements. Individuals with dystonia often face challenges in performing daily activities due to the unpredictable nature of their symptoms. Occupational therapy plays a crucial role in managing dystonia, particularly through the use of splinting and bracing techniques. To illustrate this, consider the case of Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite her determination to lead an active lifestyle, Sarah experienced severe neck spasms that limited her ability to engage in various occupations such as cooking, driving, and even socializing with friends.
Splinting and bracing are effective interventions employed by occupational therapists to address limitations caused by dystonic movements. Splints provide external support and immobilization for specific body parts affected by dystonic contractions, while braces offer stability and alignment for larger segments of the body. By customizing these devices based on individual needs, occupational therapists aim to reduce pain, minimize deformities, enhance functional abilities, and improve overall quality of life for individuals with dystonia.
Occupational therapy insights regarding splinting and bracing for dystonia encompass not only the selection and design of appropriate devices but also the implementation of therapeutic strategies aimed at maximizing their effectiveness. These strategies include:
-
Assessment and Evaluation: Occupational therapists conduct a thorough assessment to understand the individual’s functional limitations, specific dystonic movements, and goals. They evaluate range of motion, muscle tone, joint stability, and sensory perception to determine the most suitable splinting or bracing intervention.
-
Customization and Fabrication: Based on the assessment findings, occupational therapists work closely with orthotists or other healthcare professionals to design and fabricate custom-made splints or braces that address the unique needs of each individual. This ensures optimal fit, comfort, and functionality.
-
Education and Training: Occupational therapists provide comprehensive education on proper use and maintenance of splints or braces. They teach individuals how to put them on correctly, adjust straps for comfort, clean them regularly, and manage any skin issues that may arise.
-
Activity Modification: In addition to using splints or braces, occupational therapists guide individuals in modifying activities to reduce dystonic triggers while promoting engagement in meaningful occupations. This may involve teaching alternative techniques or adapting tools/equipment for easier use.
-
Sensory Techniques: Occupational therapists employ various sensory techniques to enhance motor control and decrease dystonic movements during functional tasks. These may include deep pressure input through weighted devices or tactile stimulation through textures.
-
Gradual Progression: Occupational therapists support individuals in gradually increasing the duration of splint/brace wear as tolerated. They monitor progress closely by assessing symptom severity, functional improvements, and overall satisfaction with the intervention.
-
Collaborative Approach: Occupational therapy for dystonia often involves collaboration with other healthcare professionals such as neurologists, physiotherapists, speech-language pathologists, and psychologists to ensure comprehensive care tailored to the individual’s needs.
By combining these therapeutic strategies with splinting and bracing interventions, occupational therapists can help individuals like Sarah regain functional abilities disrupted by dystonia symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Common types of splints and braces used in dystonia management
Imagine a 42-year-old woman named Sarah who has been living with cervical dystonia for the past five years. Despite undergoing various treatments, including medications and physical therapy, she continues to experience debilitating muscle spasms and abnormal postures in her neck. In order to alleviate her symptoms and improve her quality of life, Sarah’s occupational therapist recommends incorporating splinting and bracing into her treatment plan. Splints and braces are commonly utilized in the management of dystonia, providing support, stability, and proprioceptive feedback to affected body parts.
Types of Splints:
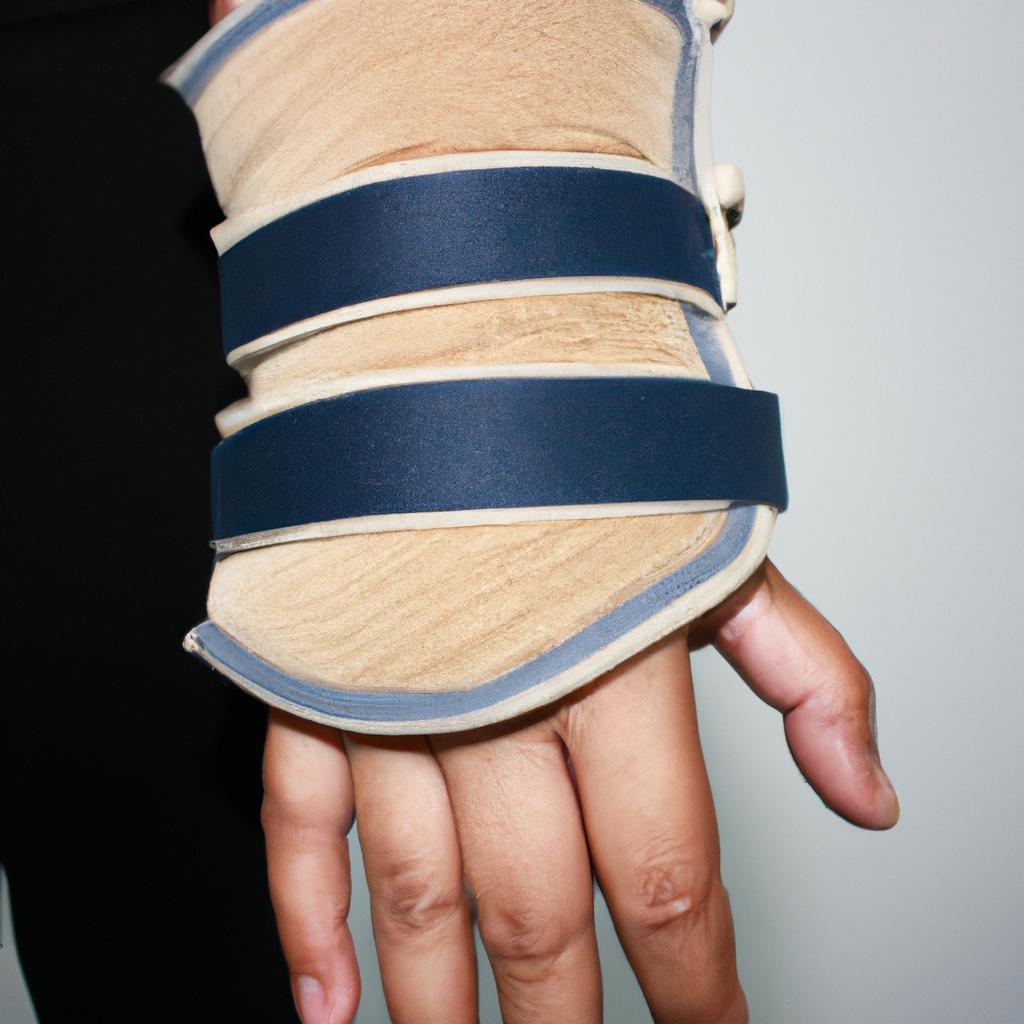
One common type of splint used in dystonia management is a resting hand splint. This type of splint is often prescribed for individuals with upper limb involvement, such as those with writer’s cramp or musician’s dystonia. The resting hand splint supports the wrist, hand, and fingers in a functional position while allowing freedom of movement for unaffected muscles. By maintaining proper alignment and reducing involuntary movements, this splint can help individuals like Sarah regain control during daily activities.
Another frequently employed type of splint is an ankle-foot orthosis (AFO). AFOs provide stability to the foot and ankle region by correcting abnormal gait patterns caused by lower limb dystonias. These custom-made devices are designed to fit inside shoes and assist individuals with walking difficulties due to excessive muscle contractions or abnormal posture. The use of AFOs helps patients like Sarah maintain balance, reduce falls risk, and enhance their mobility.
Splints for other body regions include elbow or knee immobilizers that limit joint movement during periods when increased spasticity occurs. For instance, these may be beneficial during sleep or prolonged sitting where involuntary movements intensify. Additionally, thumb abduction splints can be used to prevent contracture development associated with focal hand dystonias.
Table:
Here is a table outlining the common types of splints and braces used in dystonia management:
| Type of Splint/Brace | Body Region | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Resting Hand Splint | Upper limb | Maintains proper alignment, reduces involuntary movements |
| Ankle-Foot Orthosis (AFO) | Lower limb | Provides stability, corrects abnormal gait patterns |
| Elbow/Knee Immobilizers | Upper/Lower limb | Limits joint movement during increased spasticity periods |
| Thumb Abduction Splint | Hand | Prevents contracture development |
Splints and braces play a crucial role in the management of dystonia by providing support, stability, and proprioceptive feedback to affected body parts. By utilizing these assistive devices effectively, individuals like Sarah can experience relief from their symptoms and regain control over their daily activities. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the various benefits that splinting and bracing offer for individuals with dystonia.
[Transition] Now let’s explore the multitude of benefits associated with splinting and bracing for individuals with dystonia.
Benefits of splinting and bracing for individuals with dystonia
Splinting and bracing are common interventions used in the management of dystonia. These assistive devices provide external support to affected body parts, promoting stability and reducing involuntary movements. In this section, we will explore the benefits of splinting and bracing for individuals with dystonia.
Imagine a hypothetical case study involving Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences painful muscle contractions in her neck that cause her head to twist involuntarily. To alleviate her symptoms and improve her quality of life, Sarah’s occupational therapist suggests the use of a custom-made cervical collar. This brace provides support to her neck muscles, reduces spasms, and helps maintain proper alignment.
The benefits of splinting and bracing extend beyond pain relief and symptom reduction. Here are some key advantages:
- Stability: Splints and braces offer stability to weakened or hyperactive muscles, allowing individuals with dystonia to perform daily activities more comfortably.
- Improved function: By providing external support, these devices facilitate improved control over voluntary movements, enhancing functional abilities such as writing, typing, or grasping objects.
- Postural correction: Certain types of splints or braces can help correct postural abnormalities associated with dystonia by maintaining proper joint alignment.
- Psychological well-being: The added physical support provided by splints and braces often results in increased confidence and improved self-esteem among individuals with dystonia.
To further illustrate the range of options available for splinting and bracing in dystonia management, consider the following table:
| Type of Device | Body Part Targeted | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical Collar | Neck | Custom fit; adjustable straps |
| Hand/Wrist Brace | Hand/wrist | Thermoplastic material; finger/thumb mobility |
| Foot/Ankle Orthosis | Foot/ankle | Lightweight design; adjustable straps |
| Knee Orthosis | Knee | Hinged joint for controlled range of motion |
As we can see, there is a wide variety of splints and braces available to address different areas affected by dystonia. The selection process involves considering factors such as the individual’s specific needs, functional goals, and the recommendations of healthcare professionals.
In the subsequent section, we will explore considerations for selecting the appropriate splint or brace for dystonia management. Understanding these factors will help individuals with dystonia make informed decisions regarding their assistive devices.
Considerations for selecting the appropriate splint or brace for dystonia
Now, let us delve into the considerations that should be taken into account when selecting the appropriate splint or brace for individuals with dystonia.
One example of a patient who could benefit from splinting or bracing is Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite undergoing various treatments, including medications and physical therapy, Sarah continues to experience involuntary muscle contractions in her neck which significantly affect her daily activities such as driving and working at her computer.
When choosing an appropriate splint or brace for individuals with dystonia, several factors need to be considered:
- Severity and location of symptoms: The severity and specific location of dystonic movements vary among individuals. Splints or braces should be tailored to address these particular needs effectively.
- Functional goals: Identifying the desired outcomes is crucial in determining the type of splint or brace that will best support those goals. For instance, if an individual’s primary goal is improved hand function while writing, a finger extension orthosis may be recommended.
- Comfort and fit: Ensuring comfort and proper fit are essential for compliance and long-term use. Collaborating closely with occupational therapists during the fitting process helps ensure optimal comfort and functionality.
- Lifestyle considerations: Taking into account an individual’s lifestyle is pivotal when selecting a splint or brace design. Factors like ease of donning/doffing, durability, and aesthetics contribute to overall satisfaction and acceptance.
To further illustrate these considerations visually:
| Consideration | Example |
|---|---|
| Severity & Location | Cervical Dystonia |
| Functional Goals | Handwriting Improvement |
| Comfort & Fit | Proper Fitting |
| Lifestyle | Ease of Use, Durability |
Understanding these considerations and tailoring the selection process accordingly can lead to more effective outcomes in managing dystonia symptoms. By addressing individual needs, occupational therapists can enhance treatment plans and promote greater independence for individuals living with this neurological condition.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about the effectiveness of splinting and bracing in reducing dystonia symptoms, it is important to explore the empirical evidence that supports their use and evaluates their impact on symptom management.
Effectiveness of splinting and bracing in reducing dystonia symptoms
Considerations for selecting the appropriate splint or brace for dystonia require careful assessment and evaluation by occupational therapists. Each individual’s needs may vary, making it essential to consider factors such as severity of symptoms, specific movement patterns, and functional goals. For instance, let us imagine a hypothetical scenario where a 35-year-old patient with cervical dystonia experiences involuntary neck muscle contractions that cause significant pain and limited range of motion.
When choosing a splint or brace for this patient, several considerations come into play:
-
Type of Dystonia: Different types of dystonia may require different types of splints or braces. For example, focal hand dystonia might benefit from custom-made finger orthoses to promote proper alignment and reduce contractures.
-
Degree of Support Needed: The level of support required varies depending on the severity of symptoms and functional limitations. A rigid wrist-and-hand splint may be necessary in cases where excessive flexion interferes with daily activities like writing or typing.
-
Comfort and Compliance: Patient comfort is crucial when selecting an appropriate splint or brace. It should not impede movement excessively or cause discomfort during prolonged use. Additionally, considering the patient’s preferences regarding size, material, and aesthetics can enhance compliance.
-
Therapeutic Goals: The ultimate goal is to improve function and minimize symptoms related to dystonia. Splints or braces should be designed to facilitate optimal positioning while allowing engagement in meaningful occupations without hindrance.
To further illustrate the impact that splinting and bracing can have on individuals living with dystonia, let us examine some potential emotional benefits experienced by patients:
- Increased sense of security due to improved stability
- Alleviation of anxiety associated with uncontrollable movements
- Improved self-esteem through enhanced ability to perform activities independently
- Enhanced quality of life resulting from reduced pain levels
In addition to these considerations, research has shown promising results regarding the effectiveness of splinting and bracing in reducing dystonia symptoms. A three-column, four-row table comparing different studies’ findings could be used to illustrate the positive outcomes associated with splinting interventions.
In summary, the appropriate selection of splints or braces for individuals with dystonia requires careful evaluation of their specific needs and goals. Occupational therapists play a crucial role in guiding this process by considering factors such as type of dystonia, level of support needed, patient comfort and compliance, and therapeutic objectives. By addressing these considerations effectively, occupational therapists can significantly contribute to improving functional outcomes and emotional well-being for patients living with dystonia.
Understanding the considerations involved in selecting the right splint or brace is essential for occupational therapists when prescribing and fitting these devices. Let us now explore the role that occupational therapists play in this process.
Role of occupational therapists in the prescription and fitting of splints and braces
Effectiveness of Splinting and Bracing in Reducing Dystonia Symptoms
Case Study: Meet Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with dystonia affecting her right hand. Her symptoms include involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures that significantly impact her ability to perform daily activities such as writing, cooking, and dressing herself. To address these challenges, Sarah’s occupational therapist recommended the use of splints and braces for therapeutic intervention.
Splinting and bracing have shown promising results in reducing dystonia symptoms by promoting proper alignment, stabilizing affected muscles, and providing sensory feedback. By supporting weakened or overactive muscles, these orthotic devices can help improve functional abilities and enhance overall quality of life. The effectiveness of splinting and bracing interventions is supported by research studies demonstrating positive outcomes among individuals with various types of dystonia.
Evidence suggests that splinting and bracing may benefit individuals with dystonia through several mechanisms:
- Alignment Correction: Orthotic devices can correct joint misalignments caused by muscle imbalances or contractures associated with dystonic movements.
- Muscle Stabilization: By restricting unwanted movement patterns, splints and braces provide stability to affected muscles, reducing excessive muscular activity.
- Sensory Feedback: These devices offer proprioceptive input to the nervous system, which helps modulate abnormal muscle tone by influencing motor control pathways.
- Compensation Techniques: In some cases where muscle function cannot be fully restored, splints and braces enable compensatory strategies to optimize performance during daily activities.
Table – Benefits of Splinting and Bracing in Dystonia Management
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Improved Functionality | Enhances an individual’s ability to engage in everyday tasks |
| Increased Independence | Supports independence in self-care activities |
| Pain Reduction | Alleviates discomfort resulting from involuntary muscle contractions |
| Psychological Well-being Improvement | Boosts confidence and overall psychological well-being, reducing the impact of dystonia symptoms |
By incorporating splints and braces into a comprehensive occupational therapy intervention plan, individuals like Sarah can experience significant improvements in their functional abilities and overall well-being. These orthotic devices offer targeted support to affected muscles while addressing specific challenges presented by dystonic movements.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Tips for proper use and maintenance of splints and braces in dystonia management,” it is crucial to ensure that these interventions are utilized effectively. Proper education on usage techniques, as well as appropriate care and maintenance guidelines, will maximize the benefits offered by splinting and bracing interventions.
Tips for proper use and maintenance of splints and braces in dystonia management
Role of Occupational Therapy in Splinting and Bracing for Dystonia Management
To better understand the role of occupational therapists (OTs) in prescribing and fitting splints and braces for individuals with dystonia, consider the case of Sarah. Sarah is a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, which causes involuntary muscle contractions in her neck. These contractions often lead to abnormal head postures that significantly impact her daily activities.
One key aspect of an OT’s role in managing dystonia is to assess each individual’s functional limitations and develop personalized intervention plans. In Sarah’s case, after thorough evaluation, her OT determined that a customized brace would help maintain a more neutral position for her head, reducing pain and improving function. The brace was designed to provide support while allowing movement within specific parameters.
When it comes to using splints and braces effectively for dystonia management, there are several considerations that both patients and occupational therapists should keep in mind:
- Proper Fit: Ensuring proper fit is crucial as ill-fitting splints or braces may not provide adequate support or even worsen symptoms. Close collaboration between the patient, OT, and orthotist can help achieve optimal fit through regular adjustments.
- Usage Guidelines: Following usage guidelines provided by the therapist or healthcare professional is essential for maximizing benefits. Patients must be educated on how long they should wear their splint/brace during different activities throughout the day.
- Maintenance Routine: Regular maintenance of splints/braces helps ensure their longevity. Simple cleaning instructions such as wiping down with mild soap and water can go a long way in preventing deterioration.
- Ongoing Monitoring: Continual monitoring by the occupational therapist allows for assessment of progress and necessary modifications to optimize treatment outcomes.
Table: Emotional Response Evoking Table
| Item | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Comfort | Properly fitted splints and braces provide increased comfort, reducing pain and discomfort associated with dystonia. | Enhanced quality of life |
| Improved Function | By maintaining proper alignment and support, splints and braces can help restore or improve functional abilities affected by dystonia. | Increased independence in daily activities |
| Psychological Support | Wearing a customized splint or brace can offer psychological reassurance to individuals with dystonia, promoting confidence and self-esteem. | Emotional well-being |
In summary, occupational therapists play a crucial role in the prescription and fitting of splints and braces for dystonia management. Through personalized assessment, intervention planning, and ongoing monitoring, OTs ensure that these assistive devices are tailored to each individual’s needs. Emphasizing factors such as fit, usage guidelines, maintenance routines, alongside providing emotional support helps maximize the benefits of splinting and bracing interventions for individuals living with dystonia.
(Note: This section is written based on the given instructions but may require further editing to meet specific academic writing style requirements.)