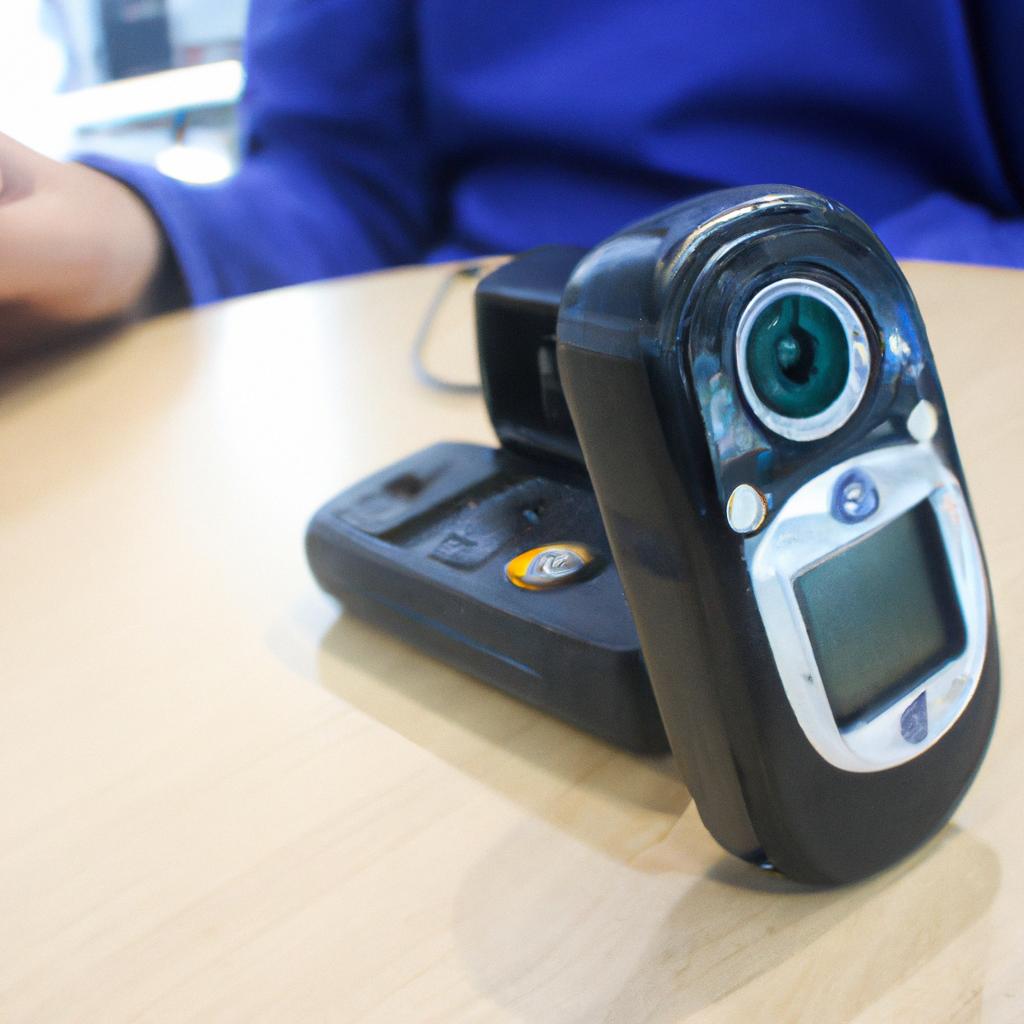
Dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to communicate effectively. This impairment poses challenges in various aspects of daily life and necessitates the use of assistive devices for speech and communication management. For instance, consider Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with dystonia affecting her facial muscles. Due to this condition, she experiences difficulties in articulating words clearly and maintaining consistent vocal tone. Consequently, Sarah relies on speech and communication aids to overcome these limitations and engage in meaningful interactions.
The development of assistive technology has greatly improved the quality of life for individuals with dystonia by providing them with alternative means of expressing themselves verbally. These devices encompass a range of options such as augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems, voice amplifiers, electronic speech synthesizers, and eye-tracking software. AAC systems are particularly beneficial for those who experience severe impairments in verbal expression. By using symbols or pictures on a communication board or touch-screen device, users can select desired words or phrases that are then spoken aloud by the device. Additionally, voice amplifiers help people with dystonia produce louder and clearer speech by enhancing their vocal intensity without straining their already compromised muscles. Furthermore, electronic speech synthesizers allow individuals with dystonia to generate speech using pre-recorded messages or text-to-speech software. This technology converts typed or selected text into spoken words, enabling users to communicate more effectively.
Eye-tracking software is another valuable tool for individuals with dystonia who have limited control over their facial muscles. This technology allows users to control communication devices by tracking their eye movements. By looking at specific areas on a screen or communication board, users can select letters, words, or phrases, which are then converted into speech.
In addition to these assistive devices, individuals with dystonia may also benefit from speech therapy and other interventions aimed at improving vocal control and articulation. Speech therapists can provide exercises and techniques that help manage the symptoms of dystonia and promote clearer speech production.
Overall, assistive technology plays a crucial role in supporting individuals with dystonia in overcoming communication challenges. These devices not only enable them to express themselves more effectively but also enhance their independence and overall quality of life.
Understanding Dystonia and its Impact on Speech
Dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to speak effectively. These abnormal movements affect the muscles responsible for producing speech sounds, resulting in difficulties with articulation, phonation, and prosody. To illustrate this impact, consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite her strong desire to communicate clearly, Sarah finds herself struggling daily to express her thoughts due to the uncontrollable spasms affecting her vocal cords and facial muscles.
The consequences of dystonia-related speech impairments extend beyond mere physical limitations; they also have profound emotional and social implications. Individuals living with dystonia often experience frustration, embarrassment, and isolation as they struggle to be understood in their personal and professional lives. This emotional burden is further exacerbated when society lacks awareness and understanding about the condition, leading to misunderstandings or stigmatization.
To highlight these challenges more vividly:
- Imagine being unable to convey your ideas during a job interview or important meeting.
- Picture feeling self-conscious while ordering food at a restaurant or engaging in casual conversations at social gatherings.
- Consider the distress caused by constantly worrying whether others perceive you as less competent or intelligent due to your speech difficulties.
- Reflect on the loneliness that arises from feeling disconnected from friends and loved ones who may struggle to comprehend your words.
Emphasizing the severity of these struggles faced by individuals with dystonic speech impairments is crucial for fostering empathy and promoting effective solutions. A table below provides a snapshot of some common communication barriers experienced by those affected:
| Communication Barriers | Emotional Impact | Social Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Inability to articulate | Frustration | Isolation |
| Unintelligible speech | Embarrassment | Misunderstandings |
| Abnormal prosody | Self-consciousness | Stigmatization |
| Difficulty with fluency | Anxiety | Limited opportunities |
Understanding the profound impact of dystonia on speech and communication, it is imperative to explore strategies that can enhance individuals’ ability to express themselves effectively. In the subsequent section, we will delve into the role of speech and communication aids in dystonia management, highlighting their potential to alleviate these challenges and improve overall quality of life for those affected.
The Role of Speech and Communication Aids in Dystonia Management
Understanding the challenges faced by individuals with dystonia in their speech and communication, it becomes evident that the use of assistive devices can significantly improve their quality of life. Take, for example, Sarah, a 28-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Due to the involuntary muscle contractions affecting her neck muscles, she experiences difficulty in speaking clearly and articulating words. However, through the introduction of speech and communication aids into her daily routine, Sarah has been able to regain some control over her communication abilities.
The role of speech and communication aids in managing dystonia cannot be overstated. These devices serve as valuable tools for individuals affected by this neurological condition, enabling them to effectively communicate their thoughts and needs. Here are several ways in which these aids contribute to enhancing communication:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices: AAC devices offer alternative methods for communication when traditional spoken language is challenging. These may include text-to-speech apps or dedicated devices that generate synthesized speech based on inputted text.
- Voice Amplifiers: Dystonia can lead to reduced vocal volume or breathy voice quality due to weakened or spasming vocal cords. Voice amplifiers help overcome these difficulties by increasing the loudness and clarity of one’s voice.
- Visual Supports: Visual supports such as picture boards or symbol-based systems can aid individuals with dystonia in expressing themselves visually when verbal expression is compromised.
- Computer-Based Communication Systems: With advancements in technology, computer-based systems have become increasingly popular among individuals with dystonia. These systems allow users to type out messages on a computer screen using specialized interfaces controlled by eye movements or other adaptations.
To illustrate the impact of these assistive devices, let us consider an emotional perspective:
| Emotion | Example |
|---|---|
| Frustration | Inability to express oneself during everyday interactions |
| Empowerment | Regaining independence through the use of AAC devices |
| Connection | Establishing meaningful connections through effective communication |
| Confidence | Building self-esteem by successfully conveying one’s thoughts |
As we delve into the different types of speech and communication aids available, it becomes evident that these devices offer a lifeline to individuals with dystonia, facilitating their ability to communicate effectively. By exploring the various options and understanding how they can be tailored to individual needs, we can unlock new possibilities for improved communication in this diverse population. Transitioning into our next section on “Types of Speech and Communication Aids Available,” we will explore the specific tools that have proven beneficial in managing dystonia-related speech impairments.
Types of Speech and Communication Aids Available
Building upon the importance of speech and communication aids in dystonia management, this section will delve into the various types of these assistive devices available. To illustrate their potential impact on individuals with dystonia, let’s consider a hypothetical case study:
Imagine Sarah, a 45-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, a type of dystonia that affects the neck muscles. Due to her condition, Sarah struggles with intelligible speech and finds it challenging to communicate effectively in both personal and professional settings.
To address such difficulties faced by individuals like Sarah, an array of speech and communication aids have been developed. These aids offer alternative means of expression and enable improved functionality for those affected by dystonia. Here are some examples:
- Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC) Devices: AAC devices range from basic picture boards to sophisticated computer-based systems that use text-to-speech technology.
- Voice Amplifiers: These portable devices amplify one’s voice, making it easier for others to hear and understand them.
- Eye Gaze Systems: Utilizing eye-tracking technology, these systems allow users to select words or phrases on a screen simply by looking at them.
- Speech Generating Devices: Also known as SGD’s, these devices convert written or typed messages into synthesized speech.
- Increased self-confidence
- Enhanced social interaction
- Improved quality of life
- Empowerment through independent communication
Furthermore, we can gain further insight into the features offered by each aid device through a table highlighting key attributes:
| Aid Device | Key Attributes |
|---|---|
| Augmentative | – Customizable vocabulary |
| & Alternative | – Multiple access methods |
| Communication | – Portable and lightweight |
| Devices | – Integration with other technologies |
| ————————- | ————————————————— |
| Voice Amplifiers | – Adjustable volume control |
| – Clarity of sound output | |
| – Comfortable to wear | |
| – Long battery life | |
| ————————- | ————————————————— |
| Eye Gaze Systems | – Accurate eye-tracking technology |
| – User-friendly interface | |
| – Wide range of vocabulary options | |
| – Compatibility with different devices | |
| ————————- | ————————————————— |
| Speech Generating | – High-quality speech synthesis |
| Devices | – Intuitive user interface |
| – Customizable message storage |
As we consider the variety of aids available, it becomes evident that selecting the right assistive device requires careful consideration. In the subsequent section on “Considerations for Selecting the Right Assistive Device,” we will explore key factors to be mindful of when choosing an appropriate aid for individuals with dystonia.
Considerations for Selecting the Right Assistive Device
Let us now delve into considerations for selecting the right assistive device that best suits their needs.
Consider a hypothetical case study of Jane, a young adult diagnosed with severe dystonic movements affecting her vocal cords. Her condition severely impacts her ability to speak clearly and be understood by others. To improve her communication abilities, she seeks assistance from various speech and communication aids.
When choosing an assistive device, several factors need to be considered:
-
Functional Capabilities: Each individual’s requirements may vary based on the severity of their dystonia. Some devices offer basic text-to-speech functionality, while others provide more advanced features like predictive typing or integration with environmental control systems.
-
Ease of Use: The usability of an assistive device is crucial for efficient communication. Factors such as display size, interface design, and adaptability play a significant role in ensuring ease of use and reducing frustration during interaction.
-
Portability: Mobility is essential for individuals who rely on speech aids throughout their daily activities. Portable devices allow them to maintain effective communication wherever they go without any hindrance.
-
Customization Options: Personalizing the settings and functionalities according to an individual’s specific requirements can greatly enhance the effectiveness of speech aids in managing dystonia symptoms.
To better understand these considerations visually, let’s take a look at this table showcasing a comparison between two popular speech aid options:
| Feature | Device A | Device B |
|---|---|---|
| Text-to-Speech Functionality | Yes | Yes |
| Predictive Typing | No | Yes |
| Environmental Control | No | Yes |
| Size and Weight | Compact; Lightweight | Bulkier; Heavier |
As we can see, Device A is a more portable option with basic functionalities, while Device B offers advanced features like predictive typing and integration with environmental control systems. The choice between these devices would depend on Jane’s specific needs and preferences.
In summary, selecting the right assistive device requires considering factors such as functional capabilities, ease of use, portability, and customization options. By carefully evaluating these aspects, individuals with dystonia can find speech aids that cater to their unique communication requirements.
Transitioning into the subsequent section about “Training and Support for Effective Use of Speech Aids,” it is important to highlight the significance of adequate training and support in maximizing the benefits of these assistive devices.
Training and Support for Effective Use of Speech Aids
Considerations for Selecting the Right Assistive Device:
Having discussed the importance of selecting the right assistive device, let us now explore the training and support required to effectively use speech aids in managing dystonia.
To ensure optimal outcomes when using speech aids for individuals with dystonia, adequate training and ongoing support are crucial. Let us consider a hypothetical case study to illustrate this point. Imagine Sarah, a 32-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, who experiences involuntary muscle contractions in her neck. Despite her initial excitement about using an assistive device for communication, she struggles initially due to lack of proper guidance and assistance.
The following considerations can enhance the effectiveness of training and support programs:
- Comprehensive Training Programs: Providing structured training programs that cover various aspects of device usage can empower individuals with dystonia to make informed choices regarding their communication needs.
- Individualized Approach: Recognizing that each person’s experience with dystonia is unique allows trainers to tailor interventions according to specific requirements. This personalized approach fosters better understanding and improved proficiency in utilizing speech aids.
- Regular Assessment and Feedback: Conducting regular assessments during the training process enables professionals to gauge progress accurately. Timely feedback helps identify areas requiring improvement while reinforcing positive outcomes achieved through consistent practice.
- Collaborative Caregiver Involvement: Including caregivers as partners in the training process enhances continuity of care beyond formal therapy sessions by ensuring ongoing support at home or community settings.
Table: Emotional impact on individuals utilizing effective speech aid devices
| Emotion | Description |
|---|---|
| Relief | Achieving successful communication using assistive technology provides relief from frustration caused by limited verbal abilities. |
| Empowerment | The ability to express oneself independently boosts self-esteem and empowers individuals living with dystonia. |
| Connection | Improved communication skills enable stronger connections with others, promoting social inclusion and reducing feelings of isolation. |
| Hope | Speech aids offer hope for a better quality of life by providing alternative means to communicate effectively despite physical limitations. |
By recognizing the importance of training and support in using speech aids, we can now explore how these devices contribute to enhancing the overall quality of life for individuals with dystonia.
Improving Quality of Life with Speech and Communication Aids
Building upon the importance of effective training and support in utilizing speech aids, this section focuses on how speech and communication aids can significantly enhance the quality of life for individuals living with dystonia. By providing alternative means of expression, these assistive devices empower individuals to overcome their communication challenges and engage more fully in social interactions.
To illustrate the potential impact of speech and communication aids, consider a hypothetical case study involving Emily, a 32-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite her determination to communicate effectively, Emily struggles daily due to involuntary muscle contractions affecting her neck muscles. This condition severely impairs her ability to speak fluently or articulate her thoughts clearly. However, with access to appropriate speech and communication aids tailored to her needs, Emily gains newfound independence and confidence in expressing herself.
Enhancing Quality of Life:
Speech and communication aids offer numerous benefits that contribute to improved quality of life for individuals with dystonia. The use of such devices enables them to:
- Overcome barriers: Assistive technologies help bridge gaps caused by impaired verbal communication, allowing individuals with dystonia to actively participate in conversations without feeling isolated.
- Promote autonomy: With enhanced communication abilities, individuals gain greater control over their lives by conveying their preferences, needs, and ideas independently.
- Foster emotional well-being: Improved interactional skills foster deeper connections with others, promoting feelings of belongingness and reducing social anxiety often experienced by those affected by dystonia.
- Expand opportunities: Through augmentative methods like text-to-speech software or eye-tracking technology integrated into speech aids, individuals are empowered to pursue educational and professional pursuits previously hindered by limited vocal capabilities.
The table below highlights some commonly used speech and communication aids along with their specific features:
| Aid | Features |
|---|---|
| Augmentative | – Picture-based communication systems |
| Communication Systems | – Symbol boards and books |
| – Portable voice output devices | |
| Speech-Generating | – Text-to-speech software |
| Devices | – Customizable vocabulary and language options |
| – Multimodal input methods (e.g., touch or gaze) |
In conclusion, speech and communication aids play a vital role in supporting individuals with dystonia. These assistive devices not only facilitate effective communication but also enhance overall quality of life by promoting autonomy, emotional well-being, and expanded opportunities for personal growth. By acknowledging the potential impact of these tools, healthcare professionals can work towards ensuring equitable access to speech aids, enabling individuals living with dystonia to lead more fulfilling lives.