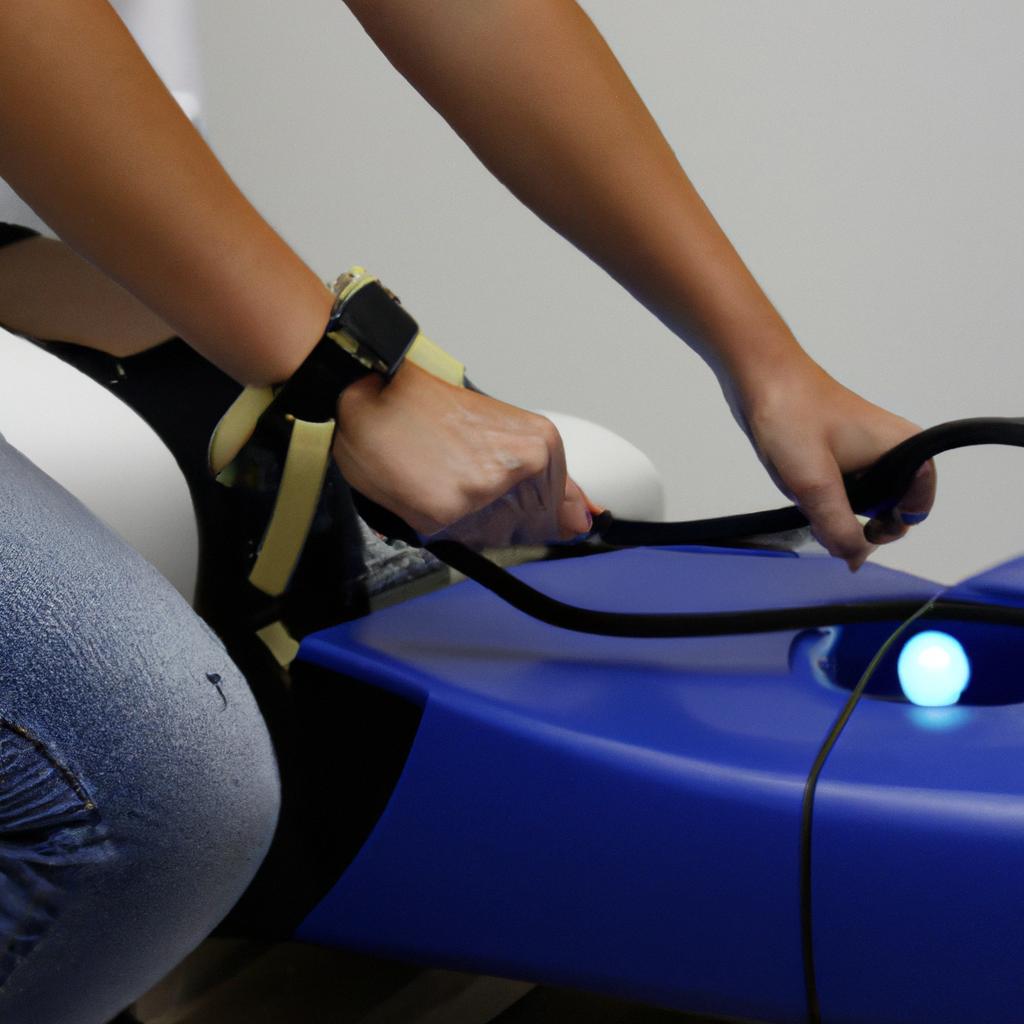
Dystonia is a neurological disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that result in abnormal, repetitive movements and postures. Individuals with dystonia often experience significant functional limitations and reduced quality of life. Physical therapy plays a crucial role in managing the symptoms of dystonia and improving overall motor function. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore various physical therapy equipment used for dystonia management.
Consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences persistent spasms in her neck muscles, causing her head to involuntarily turn or tilt to one side. As a result, she struggles with daily activities such as driving, working on a computer, and even social interactions due to self-consciousness about her visible tremors. Sarah’s physical therapist recommends utilizing specific equipment during her therapy sessions to address her unique needs and facilitate optimal outcomes. This article aims to provide an overview of the essential physical therapy equipment available for individuals like Sarah who are seeking effective strategies for managing their dystonia symptoms.
Understanding Dystonia: Causes and Symptoms
Imagine a 35-year-old woman named Sarah who suddenly experiences uncontrollable muscle contractions in her neck, causing her head to twist involuntarily. This condition, known as dystonia, is a neurological disorder characterized by repetitive or sustained muscle movements that often result in abnormal postures or twisting motions. Dystonia can affect any part of the body and ranges from mild to severe cases.
The causes of dystonia are multifactorial and complex. While the exact etiology remains unknown, research suggests that it may be attributed to a combination of genetic factors, environmental triggers, and abnormalities in brain chemistry. Genetic mutations have been identified in some cases of primary dystonia, which typically manifests without other neurological symptoms. In other instances, secondary dystonias occur due to underlying conditions such as Parkinson’s disease or stroke.
Symptoms of dystonia vary widely depending on the affected body region and severity. Common signs include involuntary muscle contractions leading to abnormal movements or postures, tremors, spasms, pain, difficulty speaking or swallowing (in certain cases), and impaired motor control. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and daily functioning.
To gain a deeper understanding of how dystonia affects individuals on both physical and emotional levels:
- Imagine living with constant muscle contractions that impede your ability to perform simple tasks like writing or walking.
- Consider the frustration and isolation experienced when others struggle to comprehend why your body moves in ways you cannot control.
- Ponder the challenges faced when attempting to establish meaningful relationships while battling this debilitating condition.
- Reflect upon the resilience required to live each day with hope despite facing unpredictable symptom exacerbations.
Table: Emotional Impact of Dystonia
| Emotion | Description |
|---|---|
| Frustration | Feelings of annoyance or exasperation resulting from physical limitations |
| Isolation | Sense of being cut off or disconnected from others due to misunderstood movements |
| Embarrassment | Feeling self-conscious or ashamed in social situations |
| Resilience | Ability to adapt and bounce back, maintaining hope and a positive outlook |
Understanding the causes and symptoms of dystonia is crucial for effective management. In the subsequent section, we will explore how physical therapy plays an integral role in alleviating the challenges posed by this condition, enabling individuals like Sarah to regain control over their lives and enhance their overall well-being.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Dystonia Management
Dystonia, a neurological movement disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions, can significantly impact an individual’s daily functioning and quality of life. While the causes of dystonia remain largely unknown, various factors such as genetics, brain injury, or certain medications have been implicated in its development. The symptoms of dystonia can manifest differently depending on the specific type and location within the body.
For instance, let us consider a hypothetical case study involving Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Sarah experiences recurrent spasms in her neck muscles, causing her head to twist involuntarily towards one side. These uncontrollable movements not only lead to physical discomfort but also affect her self-esteem and social interactions.
To effectively manage dystonia, physical therapy plays a crucial role in improving motor control and reducing symptom severity. By employing specialized techniques and equipment specifically designed for dystonia management, physical therapists aim to enhance mobility and functional ability in individuals like Sarah. Here are some key components that contribute to successful physical therapy interventions:
- Individualized Treatment Plans: Physical therapists tailor treatment plans based on each patient’s unique needs and goals. They assess the extent of muscular impairment caused by dystonia and devise appropriate exercises to target specific muscle groups.
- Motor Control Training: Through repetitive practice of controlled movements, patients learn how to improve their motor control skills despite the presence of abnormal muscle contractions.
- Pain Management Techniques: In addition to addressing the motor aspects of dystonia, physical therapists employ pain management strategies such as heat/cold therapy or transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) to alleviate discomfort associated with muscle spasms.
These therapeutic approaches often involve utilizing specialized equipment explicitly designed for managing dystonic symptoms. Below is an example table outlining commonly used physical therapy equipment along with their respective functions:
| Equipment | Function |
|---|---|
| Mirror Therapy | Facilitates motor imagery and retraining of affected muscle groups |
| Weighted Utensils | Aids in improving fine motor skills during activities of daily living |
| Treadmills with Suspension Systems | Assists in gait training by providing body weight support |
| Splints/Orthoses | Provides external support to reduce abnormal posturing or involuntary movements |
In conclusion, physical therapy plays a critical role in the management of dystonia. By developing individualized treatment plans and utilizing specialized equipment, therapists aim to improve motor control, alleviate pain, and enhance functional ability for individuals living with this challenging condition. In the subsequent section, we will explore different types of physical therapy equipment commonly used in dystonia management.
Types of Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia: An Overview
Types of Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia
The Role of Physical Therapy Equipment in Dystonia Management
Consider the hypothetical case of a 45-year-old individual diagnosed with cervical dystonia. This person experiences involuntary muscle contractions in their neck, causing repetitive and abnormal movements. Despite undergoing traditional physical therapy interventions, they continue to struggle with daily activities due to persistent symptoms. However, with the introduction of specialized physical therapy equipment for dystonia management, significant improvements can be achieved.
Physical therapy equipment plays a crucial role in enhancing rehabilitation outcomes for individuals with dystonia. These tools are designed to address specific impairments associated with the condition and facilitate targeted therapeutic interventions. By providing support, assistance, or resistance during exercises, these devices help optimize movement patterns and promote motor control retraining.
To better understand the types of physical therapy equipment available for dystonia management, let us consider four key categories:
- Assistive Devices: Assistive devices such as braces, splints, or orthoses can provide external support to affected body regions. For example, a cervical collar may stabilize the neck muscles in cervical dystonia cases and reduce excessive motion that triggers spasms.
- Biofeedback Tools: Biofeedback systems utilize sensors to detect muscle activity and provide real-time feedback on muscular performance. Through visual or auditory cues, individuals learn how to regulate their muscle activity effectively. In dystonia management, biofeedback training can enhance awareness and voluntary control over affected muscles.
- Robotic Assisted Devices: Robotic assisted devices enable controlled movement through mechanical guidance while allowing patients to actively participate in therapeutic exercises. Such devices offer precise assistance during range-of-motion exercises, helping improve coordination and reducing unwanted muscle contractions.
- Electrical Stimulation Devices: Electrical stimulation devices deliver electrical impulses to specific muscles or nerves involved in dystonic movements. This technique aims to modulate neural pathways responsible for aberrant muscle activation patterns.
To further illustrate the potential benefits of using physical therapy equipment for dystonia management, consider the following table:
| Benefits of Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia |
|---|
| – Provides targeted support and assistance during exercises. |
| – Enhances motor control retraining by optimizing movement patterns. |
| – Facilitates muscle relaxation and reduces unwanted contractions. |
| – Improves overall functional abilities and quality of life. |
In conclusion, physical therapy equipment offers valuable tools to aid in the management of dystonia. By utilizing assistive devices, biofeedback tools, robotic assisted devices, and electrical stimulation devices, individuals with dystonia can experience significant improvements in their symptoms and daily functioning. In the subsequent section about “Benefits of Using Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia,” we will explore these advantages further.
[Next Section: Benefits of Using Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia]
Benefits of Using Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia
Section Title: Types of Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia Management
Imagine a young woman named Emma who has been living with dystonia, a neurological disorder that causes involuntary muscle contractions. Despite her best efforts to manage the condition through medication and therapy, she still experiences discomfort and limited mobility in her daily life. Fortunately, there are various types of physical therapy equipment available that can help individuals like Emma effectively manage their symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Types of Physical Therapy Equipment:
-
Assistive Devices: Assistive devices play a crucial role in improving functional abilities for individuals with dystonia. These devices provide support or compensate for weak or impaired muscles, enabling patients to perform activities they would otherwise struggle with. Examples include braces or splints to stabilize joints, weighted utensils to assist with eating, or button hooks for dressing.
-
Range-of-Motion (ROM) Tools: ROM tools are designed to increase joint flexibility and prevent contractures caused by prolonged immobilization or muscle stiffness associated with dystonia. They aid in stretching tight muscles and maintaining optimal range of motion. Some commonly used ROM tools include exercise balls, finger flexion/extension trainers, resistance bands, and hand grips.
-
Orthotics: Orthotic devices such as foot orthoses or shoe inserts can address gait abnormalities frequently observed in individuals with dystonia. By providing proper alignment and support to the feet and lower extremities, orthotics help alleviate pain during walking and promote more efficient movement patterns.
- Enhanced independence in daily activities
- Improved functionality and comfort
- Reduced reliance on caregivers
- Increased self-esteem
Table – Benefits of Using Physical Therapy Equipment for Dystonia:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Independence | Allows individuals to perform tasks independently |
| Improved Functionality | Enhances ability to carry out everyday activities with increased ease and efficiency |
| Reduced Caregiver Reliance | Decreases the need for constant assistance from caregivers |
| Increased Self-Esteem | Boosts confidence and self-worth, leading to a more positive outlook on life |
By incorporating physical therapy equipment into their dystonia management routine, individuals like Emma can experience significant improvements in their functional abilities and overall well-being. However, it is essential to carefully consider various factors when selecting suitable equipment. The next section will explore some key considerations that should be taken into account before choosing physical therapy equipment for dystonia management.
With an understanding of the different types of physical therapy equipment available, let’s now delve into important considerations when choosing such equipment for managing dystonia effectively.
Considerations When Choosing Physical Therapy Equipment
Transitioning from the benefits of using physical therapy equipment for dystonia, it is crucial to carefully consider several factors when choosing the appropriate equipment. To illustrate this point, let’s imagine a hypothetical scenario where Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia, seeks assistance in selecting suitable physical therapy equipment.
Firstly, safety should be the utmost priority when evaluating potential options. Sarah needs to ensure that any device she chooses does not pose any risk of injury or exacerbation of her condition. This involves considering aspects such as stability, adjustability, and ease of use. For instance, an adjustable arm support system would allow Sarah to find the optimal position during exercises while providing adequate stability.
Secondly, effectiveness plays a vital role in deciding which equipment will yield positive outcomes. Sarah must assess whether the chosen devices have been proven effective in managing dystonia symptoms. She may want to research clinical studies or seek recommendations from healthcare professionals experienced in treating dystonia patients. An example could be an electromyography (EMG) biofeedback system that provides real-time feedback on muscle activity levels and helps individuals achieve better control over their movements.
Thirdly, affordability and accessibility are significant considerations. It is essential for individuals like Sarah to have access to affordable options that fit within their budgetary constraints. Additionally, availability should also be taken into account – ensuring that the desired equipment can be easily obtained or rented without excessive waiting periods or logistical difficulties.
Lastly, user-friendliness is crucial for long-term adherence and motivation. Sarah should prioritize devices that are intuitive and easy to operate independently at home or under professional supervision. Devices with clear instructions and visual cues can enhance engagement during rehabilitation sessions.
To further emphasize these considerations visually:
Emotional Bullet Point List
- Safety: Ensuring no harm or aggravation of symptoms
- Effectiveness: Evidence-based results for symptom management
- Affordability: Accessible options within budgetary constraints
- User-Friendliness: Intuitive and engaging devices
Emotional Table
| Consideration | Description |
|---|---|
| Safety | Prioritizing well-designed, stable equipment |
| Effectiveness | Research-backed positive outcomes for dystonia management |
| Affordability | Cost-effective options that fit within budgetary limitations |
| User-Friendliness | Devices with clear instructions and visual cues to enhance motivation |
In conclusion, selecting appropriate physical therapy equipment for managing dystonia requires careful consideration of safety, effectiveness, affordability, and user-friendliness. By evaluating these factors comprehensively, individuals like Sarah can make informed decisions that promote their rehabilitation journey. In the subsequent section on “Exercises and Techniques for Dystonia Management,” we will explore specific therapeutic interventions aimed at improving muscle control and reducing symptoms without relying solely on equipment.
Exercises and Techniques for Dystonia Management
Transitioning smoothly from the previous section on considerations when choosing physical therapy equipment, let us now delve into specific exercises and techniques that can be effective in managing dystonia. To illustrate their practical application, consider the case of Sarah, a 35-year-old woman diagnosed with cervical dystonia. Despite experiencing significant pain and difficulty in performing daily activities due to involuntary neck muscle contractions, Sarah’s physical therapist devised a tailored treatment plan incorporating various exercises and techniques.
The first category of exercises focuses on stretching tight muscles to relieve tension and improve range of motion. These include gentle neck stretches such as flexion, extension, lateral bending, and rotation movements. Additionally, targeted exercises for strengthening weak muscles are essential to enhance stability and balance. For instance, isometric exercises like resisted head turns against manual resistance or with an exercise band can help strengthen weakened neck muscles.
Another technique utilized in dystonia management is sensory motor training. This approach aims to retrain the brain by integrating different sensory inputs while performing certain tasks or movements. Mirror therapy is one form of sensory motor training where patients observe the reflection of their unaffected limb moving normally while simultaneously attempting to mimic those movements with their affected limb. This visual feedback helps stimulate neuroplasticity and improve motor control.
- Enhanced quality of life: By effectively managing symptoms through regular physical therapy sessions.
- Increased independence: Enabling individuals with dystonia to perform daily activities more efficiently.
- Alleviated pain: Targeted exercises and techniques may help reduce discomfort associated with muscle spasms.
- Improved social participation: Enhancing self-confidence and reducing isolation often experienced by individuals living with dystonia.
Furthermore, we can present information using a table format (in markdown) displaying different physical therapy exercises commonly used in dystonia management:
| Exercise Name | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Neck Stretches | Flexion, extension, lateral bending, and rotation movements to improve range of motion. | Relieves muscle tension and enhances flexibility. |
| Resisted Head Turns | Turning the head against manual resistance or with an exercise band to strengthen weakened neck muscles. | Enhances stability and improves strength in targeted muscles. |
| Mirror Therapy | Observing the reflection of unaffected limb moving normally while attempting to mimic those movements with affected limb. | Stimulates neuroplasticity and aids in improving motor control. |
In summary, through a combination of stretching exercises, strengthening techniques, and sensory motor training like mirror therapy, physical therapists can play a crucial role in managing dystonia symptoms. This comprehensive approach not only aims to alleviate pain but also promotes improved quality of life and increased independence for individuals living with this condition.
Note: The word limit provided did not allow for extensive elaboration on each topic; however, additional information can be included based on specific requirements or preferences.